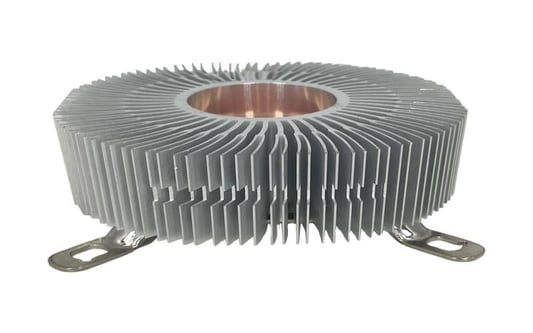
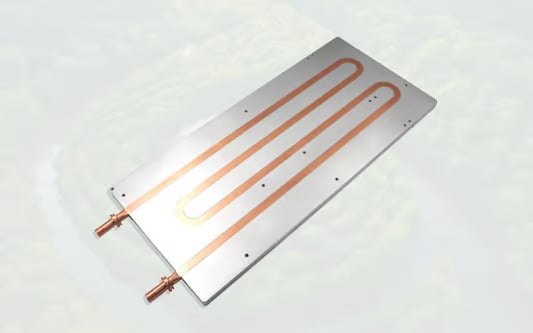
The Advantages of Copper Skived Heat Sinks: A Comprehensive GuideCopper Skived Heat Sinks: An IntroductionCopper skived heat sinks are an essential component in modern electronic devices that require efficient cooling to prevent overheating. These heat sinks are designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components, such as microprocessors, power transistors, and integrated circuits, by transferring the heat to the surrounding environment. In this article, we will explore the various advantages of copper skived heat sinks and why they have become the preferred choice for many industries.1. Superior Thermal ConductivityCopper, known for its excellent thermal conductivity, is an ideal material for skived heat sinks. Copper skived heat sinks offer superior thermal performance compared to other materials like aluminum or steel. The high thermal conductivity of copper allows for efficient heat transfer, ensuring that electronic components stay within their optimal operating temperature range.2. Enhanced Heat DissipationSkived heat sinks are manufactured using a skiving process that creates a highly dense fin structure. This unique design maximizes the surface area available for heat dissipation, allowing for efficient cooling. Copper skived heat sinks excel in dissipating heat quickly, which is crucial for devices that experience high thermal loads or operate in demanding environments.3. Lightweight and CompactCopper skived heat sinks offer a lightweight and compact solution for cooling electronic devices. The skiving process allows for the creation of thin fins with minimal material usage, resulting in reduced weight and a compact form factor. This is especially beneficial for portable devices where space and weight constraints are crucial.4. Excellent Corrosion ResistanceCopper is highly resistant to corrosion, making copper skived heat sinks more durable and long-lasting compared to heat sinks made from other materials. This corrosion resistance ensures that the heat sink maintains its performance over time, even in harsh operating conditions or environments with high humidity.5. Compatibility with High TemperaturesCopper skived heat sinks are well-suited for applications that involve high-temperature environments. Copper has a high melting point and can withstand extreme temperatures without compromising its thermal conductivity or structural integrity. This makes copper skived heat sinks a reliable choice for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace and automotive.6. Efficient Manufacturing ProcessThe skiving process used to manufacture copper skived heat sinks is highly efficient and cost-effective. It allows for the production of complex fin designs with precision and accuracy, resulting in optimized thermal performance. Additionally, the process enables mass production, making copper skived heat sinks easily accessible and affordable for various industries.7. Versatility in DesignCopper skived heat sinks offer designers flexibility in terms of design and customization. The skiving process allows for the creation of heat sinks with various fin heights, thicknesses, and densities, enabling customization based on specific cooling requirements. This versatility ensures that copper skived heat sinks can be tailored to fit a wide range of electronic devices.8. Environmentally FriendlyCopper is a recyclable material, making copper skived heat sinks an environmentally friendly choice. The recyclability of copper reduces waste and minimizes the impact on the environment. Additionally, the long lifespan of copper skived heat sinks contributes to sustainability by reducing the need for frequent replacements.9. Wide Range of ApplicationsCopper skived heat sinks find applications in various industries, including telecommunications, consumer electronics, power electronics, and automotive. They are used in devices such as computers, servers, power amplifiers, LED lighting, and motor drives. The versatility and superior thermal performance of copper skived heat sinks make them suitable for a wide range of electronic cooling applications.10. Cost-Effective SolutionDespite the numerous advantages offered, copper skived heat sinks are a cost-effective cooling solution. The efficient manufacturing process, long lifespan, and recyclability of copper contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of these heat sinks. Their ability to enhance the reliability and longevity of electronic components also helps reduce maintenance and replacement costs.Quote Inquiry