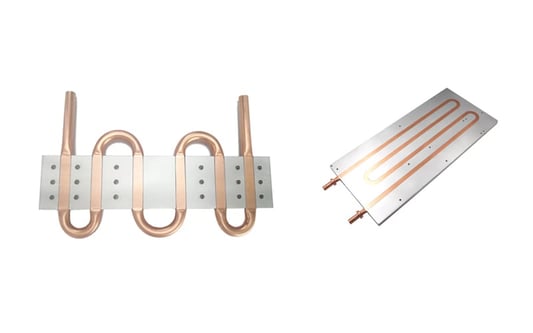
Enhanced Thermal ManagementLiquid cold plate technology provides efficient thermal management solutions for aerospace industry, allowing for better heat dissipation and temperature control in critical components.Increased Performance and ReliabilityBy utilizing liquid cooled systems, aerospace equipment can operate at optimal performance levels, reducing the risk of overheating and improving overall reliability.Weight ReductionCompared to traditional air cooling systems, liquid cold plates are lightweight and compact, helping to reduce the overall weight of aerospace vehicles while maintaining efficient cooling.Space-saving DesignThe compact design of liquid cold plate technology allows for more efficient use of space within aerospace equipment, maximizing functionality without sacrificing performance.Longevity and DurabilityLiquid cold plates are known for their durability and long service life, making them a cost-effective solution for the aerospace industry that can withstand harsh operating conditions.Energy EfficiencyWith improved thermal management, liquid cold plate technology can help reduce energy consumption in aerospace applications, contributing to environmental sustainability.Improved System IntegrationIntegrating liquid cold plates into aerospace systems is relatively straightforward, allowing for seamless compatibility with existing components and technologies.Customization and FlexibilityLiquid cold plates can be customized to meet the specific requirements of aerospace applications, providing flexibility in design and optimization for different needs.Cost-effectivenessWhile liquid cold plate technology may have higher upfront costs, its long-term benefits in terms of performance, reliability, and energy efficiency make it a cost-effective choice for the aerospace industry.Future Advancements and InnovationsOngoing research and development in liquid cold plate technology continue to drive advancements in thermal management solutions for the aerospace industry, promising even greater benefits in the future.Quote InquiryContact us