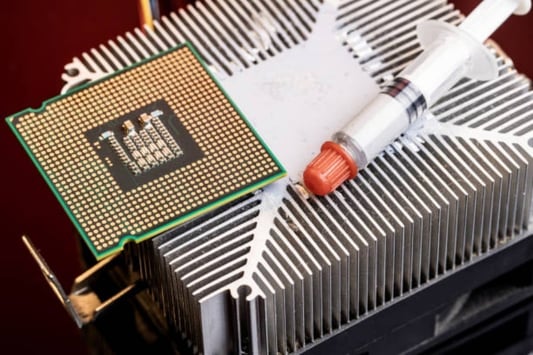
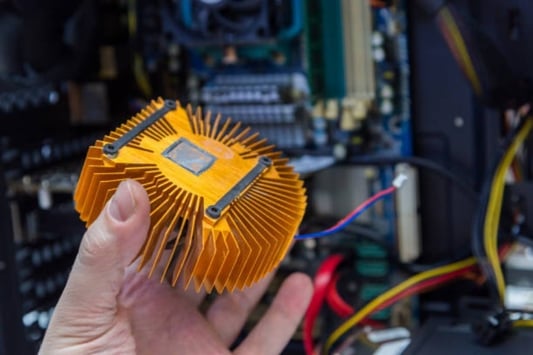
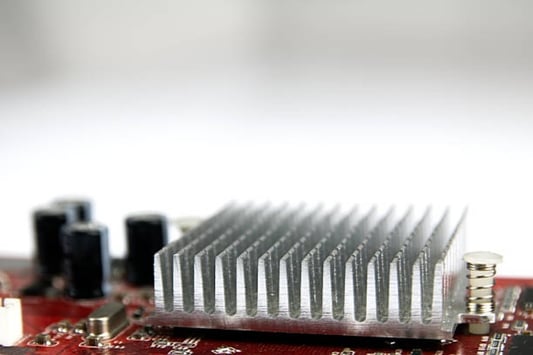
The Significance of motherboard m 2 heatsink for PC coolingWhen building a gaming PC, the components you choose matter as much as assembling it correctly. One of the critical components is the motherboard, responsible for connecting all the essential hardware taking the essential cooling system that keeps your computer functioning. Therefore, a motherboard m 2 heatsink is an essential component that removes excess heat from the M.2 solid-state drive, preventing that component from dropping the embedded controllerWhat is a motherboard M 2 heatsink?The M.2 interface is a new standard that provides a faster connection than traditional solid-state drives (SSDs) use. These SSDs tend to grow adept at high temperatures. Additionally, if they reach too high temperatures, the system may crash, leading to possible data loss, among other issues. Therefore, motherboard manufacturers have developed various methods, including adding a heatsink on the M.2 slots, leading to improved thermal performance and better data transfers.Why does your motherboard need an M 2 Heatsink?The M.2 solid-state drives have a chip that runs hotter than the other components within the system. When it runs hot, it can cause thermal throttling or damage to the performance over time. Additionally, the heat can impact other components in your system, ultimately leading to sluggish performance or failing drives. Therefore, adding a heatsink on your motherboard prevents hot spots from occurring when transferring high-speed data-intensive operations.The Benefits of a motherboard M 2 HeatsinkEnhanced functionality: A motherboard M 2 heatsink helps improve the efficiency of your computer components. This component rapidly absorbs excess heat, allowing all the systems inside the computer to run at optimal temperature levels, ensuring no heat interference in the smooth functioning of the other components. Long-lasting hardware: Excessive heat can damage the circuits, thus rendering a hard drive or other components completely useless. A Motherboard M 2 heatsink generates a significant decrease in your SSD drives' operating temperatures, such that the SSD may last longer, protecting your significant investment in the components that merchant enormous amounts of data. Effortless installation: Motherboard M 2 heatsinks is relatively simple to install. For some motherboards, generally, aftermarket heatsinks tend to avoid active cooling, potentially making repairs or modifications problematic in the future. Therefore, choosing compatible heatsinks ensures simple installation, no additional cables, software, or complicated installation techniques required. Heatsink Design and compatibilityThe size of an M.2 solid-state drive and its slot are compatible with the PCIE interface, which can become a bottleneck. The heatsink designs vary for different brands, which is why choosing the correct heatsink keeping compatibility with the motherboard's manufacturer is critical. A proper heatsink design ensures that your M.2 solid-state drive reliably maintains excellent heat dissipation.The types of Heatsinks for Motherboard M 2Passive Heatsinks: These heatsinks are usually made of metal; they dissipate heat passively using a series of ridges, fins, and air pockets. Passive heatsinks often come with adhesive or screws, allowing the mounting of M.2 drives directly. Their design can easily fit in your computer components and run silently if active cooling does not fit your setup requirements. Active Heatsinks: These heatsinks use an electric fan to circulate air over the surface to keep the M.2 drive cool. They come with a small fan attached directly on top of the heatsink or use the power from an adjacent USB slot. This option can provide better sustained cooling for your M.2 drives and decrease temperatures more effectively in a tight computer case. Installation Guide for Motherboard M 2 HeatsinkBefore installation, make sure you have the correct physical support for your M.2. Follow the installation steps as required by the motherboard's manufacturer. Below are basic guidelines that might help ease the process:Locate the M.2 slots- Depending on your motherboard, slots may be labeled differently; check the motherboard manual.Remove the adhesive plastic backing on the heatsink Position the heatsink over the installed M.2 drive, and then firmly press it down on the exposed surface. Ensure that the metal portion of the heatsink is in direct contact with the center of the SSD for maximum cooling. Double-check the placement, fasten the screws to lock the heatsink in place, and connect the fan (if applicable). Remember to take precaution not to over-tighten the screws and to handle the delicate M.2 drive with utmost care during the process. ConclusionThe Motherboard M 2 heatsink has become an essential component of a gaming PC setup. Whichever SSD or motherboard you use, the provision for a Blu-ray or NVME support system is excellent. It enables the system to function at optimal temperatures and ensures that you have longer hardware life while keeping your investment intact. Choosing the right heatsink design and correctly installing it on your system is vital in ensuring maximum performance of your computer components.Quote Inquiry