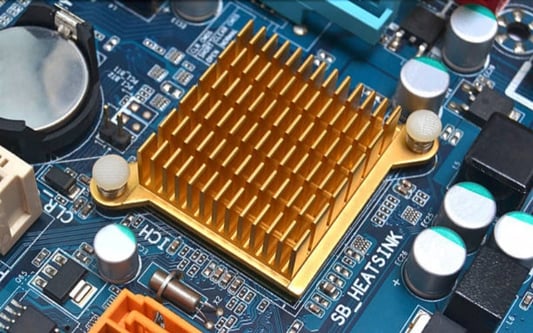
Which is Better: Copper or Aluminum Heat Sink?When it comes to choosing the right heat sink for your electronic devices, one of the most important decisions you'll need to make is whether to use copper or aluminum. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of copper and aluminum heat sinks, helping you determine which is better suited for your specific needs.The Advantages of Copper Heat SinksCopper has long been a popular choice for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity. This means that copper can efficiently transfer heat away from the electronic components it is in contact with, helping to keep them cool. Copper is also a highly durable material, resistant to corrosion and offering excellent mechanical strength. Another advantage of copper heat sinks is their compatibility with different soldering techniques, making them easier to integrate into your device's design.The Advantages of Aluminum Heat SinksWhile copper may be the traditional choice, aluminum heat sinks have gained popularity in recent years for several reasons. One of the primary advantages of aluminum is its lower cost compared to copper. Aluminum is also lightweight, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern. Additionally, aluminum heat sinks can be manufactured using extrusion, allowing for complex designs and customization options. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity, although it is not as efficient as copper in this regard.Thermal Conductivity: Copper vs. AluminumThermal conductivity is a crucial factor to consider when choosing a heat sink material. Copper has a thermal conductivity of around 401 W/mK, making it one of the best conductors of heat among common metals. Aluminum, on the other hand, has a lower thermal conductivity of approximately 205 W/mK. While copper clearly outperforms aluminum in terms of thermal conductivity, the difference may not be significant for some applications. It is important to consider the specific heat dissipation requirements of your device before making a decision.Weight and Size ConsiderationsAnother important aspect to consider when choosing between copper and aluminum heat sinks is the weight and size of the heat sink. Copper heat sinks are generally heavier than aluminum heat sinks, which may be a concern if weight is a critical factor in your application. Aluminum, being lighter, can be preferred in situations where reducing weight is essential. Additionally, aluminum heat sinks can be manufactured with thin fins, allowing for better surface area and enhanced heat dissipation.Cost Comparison: Copper vs. AluminumCost is often a significant factor in any manufacturing decision, and heat sinks are no exception. Copper is generally more expensive than aluminum, primarily due to the higher cost of the raw material. However, it is important to consider the overall cost-effectiveness of the heat sink, taking into account factors such as its performance, durability, and lifespan. While copper may have a higher upfront cost, it may provide better long-term value due to its superior thermal conductivity and durability.Corrosion Resistance and DurabilityWhen considering the durability of a heat sink, both copper and aluminum have their respective advantages. Copper is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh environments, making it suitable for applications where the heat sink may be exposed to moisture or other corrosive elements. Aluminum, on the other hand, is more susceptible to corrosion but can be protected with various surface treatments such as anodization or powder coating. Properly coated aluminum heat sinks can offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance.Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) ShieldingIn some applications, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding is a critical requirement. Copper has superior EMI shielding capabilities compared to aluminum. Its high electrical conductivity allows it to effectively block electromagnetic waves and prevent interference. If EMI shielding is a primary concern for your application, copper heat sinks may be the better choice.Manufacturing Complexity and CustomizationAluminum heat sinks offer advantages in terms of manufacturing complexity and customization options. Aluminum can be easily extruded, allowing for intricate designs and complex shapes. This flexibility makes aluminum heat sinks suitable for applications where specific thermal requirements or space constraints need to be met. Copper, on the other hand, is more challenging to work with and may limit design options.The Bottom Line: Choosing the Right Heat SinkSo, which is better, copper or aluminum heat sink? Ultimately, the answer depends on your specific needs and requirements. Copper heat sinks offer excellent thermal conductivity, durability, and EMI shielding capabilities, but they come at a higher cost. Aluminum heat sinks, on the other hand, are lightweight, cost-effective, and offer flexibility in design. Consider factors such as thermal conductivity, weight, cost, durability, and customization options when making your decision. It may also be beneficial to consult with a thermal management expert to ensure you choose the heat sink material that best suits your application.Quote InquiryContact us!