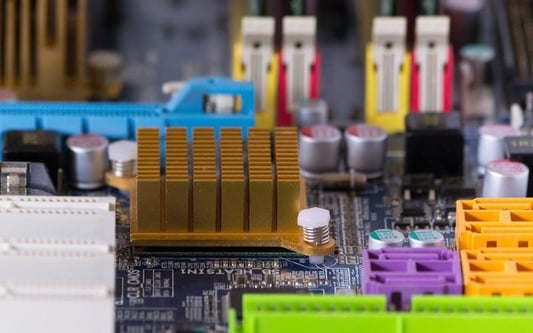
Understanding the Importance of a HeatsinkWhen it comes to building a high-performance computer or electronic device, one of the key components you need to consider is the heatsink. A heatsink is designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components, helping to prevent overheating and potential damage. Finding a compatible heatsink is crucial for ensuring optimal thermal management in your system.Consider the Type of Processor or ChipThe first step in finding a compatible heatsink is to consider the type of processor or chip you are using in your system. Different processors require different heatsinks based on their thermal design power (TDP) and socket type. Be sure to check the specifications of your processor before choosing a heatsink.Look at the Socket Type of Your MotherboardIn addition to the processor type, you also need to consider the socket type of your motherboard. Heatsinks are specifically designed to fit onto certain socket types, so it's important to match the heatsink with the socket on your motherboard. Common socket types include LGA1151, AM4, and LGA2066.Check the Clearance in Your SystemAnother important factor to consider when choosing a heatsink is the clearance in your system. Make sure that the heatsink you choose fits within the dimensions of your case and does not interfere with other components such as RAM modules or graphics cards. Measure the clearance in your system before making a purchase.Think About Your Cooling NeedsDifferent heatsinks offer different levels of cooling performance. If you have a high-performance system that generates a lot of heat, you may want to opt for a larger heatsink with more cooling fins and a higher fan speed. Consider your cooling needs based on the components in your system.Consider the Noise LevelSome heatsinks come with fans that can be quite noisy, especially at higher speeds. If noise is a concern for you, look for heatsinks with quieter fans or consider investing in a fanless heatsink. Keep in mind that fanless heatsinks may not offer the same level of cooling performance as those with fans.Check the Material and Build QualityThe material and build quality of a heatsink can also impact its performance and durability. Copper heatsinks are known for their excellent thermal conductivity, while aluminum heatsinks are more lightweight. Look for a heatsink that is well-built and designed to last.Consider Overclocking PotentialIf you are planning to overclock your system for higher performance, you will need a heatsink that can handle the increased thermal load. Look for heatsinks that are specifically designed for overclocking and offer better heat dissipation capabilities. Make sure to choose a heatsink that can keep up with your overclocking ambitions.Read Reviews and Seek RecommendationsBefore making a final decision, take the time to read reviews and seek recommendations from other users or experts in the field. They can provide valuable insights into the performance and compatibility of different heatsinks. Look for feedback on factors such as ease of installation, cooling performance, and build quality.Ensure Proper InstallationOnce you have found a compatible heatsink for your system, make sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper installation. Improper installation can lead to reduced cooling efficiency and potential damage to your components. Take your time and ensure that the heatsink is securely attached and making proper contact with the processor.Quote InquiryContact us!