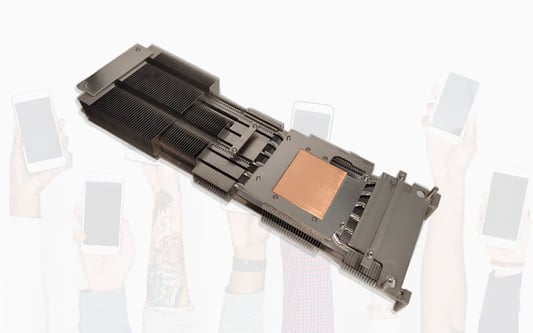
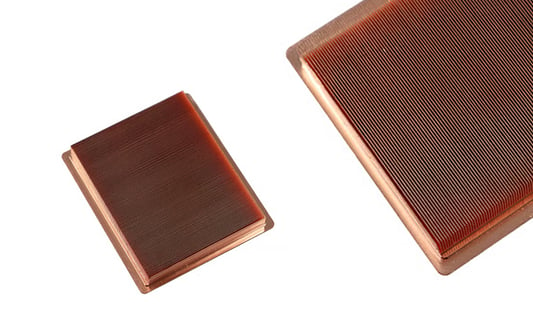
Understanding the Basics of Heat SinkA heat sink is a crucial component used in electronic devices to dissipate heat and prevent overheating. It is commonly found in computers, laptops, smartphones, and other electronic devices. In this article, we will explore how a heat sink works and its importance in maintaining optimal performance and longevity of electronic devices.What is a Heat Sink?A heat sink is a passive cooling device that absorbs and dissipates heat generated by a specific component, such as a processor or a graphics card, by increasing its surface area. It is typically made of a thermally conductive material, usually aluminum or copper, which efficiently transfers heat away from the source.Conduction: The Key PrincipleAt the core of a heat sink's functionality is the principle of conduction. Heat flows from a hotter object to a cooler object through direct contact. The heat sink's main objective is to provide a large surface area in contact with the heat-generating component to facilitate the transfer of heat.The Importance of Surface AreaIncreasing the surface area allows the heat sink to dissipate heat more effectively. The larger the surface area, the more heat can be transferred to the surrounding environment. Heat sinks often feature fins or ridges to maximize surface area, ensuring efficient heat dissipation.The Role of Thermal Interface Material (TIM)Thermal Interface Material, commonly known as TIM, is a crucial component in heat sink installation. It is a substance applied between the heat sink and the heat-generating component to improve thermal conductivity and eliminate air gaps. Common materials used as TIM include thermal paste, thermal pads, and phase change materials.Understanding Airflow and Heat DissipationAirflow plays a vital role in heat dissipation. Heat sinks are designed to work in conjunction with fans or natural convection to enhance the cooling process. The primary objective is to create a continuous flow of air over the heat sink's fins, allowing heat to be carried away from the device.The Difference Between Active and Passive Heat SinksHeat sinks can be categorized as either active or passive. Active heat sinks utilize fans or blowers to force air across the fins, increasing the cooling efficiency. Passive heat sinks rely solely on natural convection, making them quieter but less effective in dissipating heat compared to active heat sinks.Optimizing Heat Sink DesignHeat sink design plays a crucial role in its effectiveness. Factors such as fin density, fin thickness, and base materials impact the overall thermal performance. Engineers carefully consider these design aspects to ensure the heat sink is tailored to the specific requirements of the device it is intended for.Other Cooling SolutionsWhile heat sinks are widely used in electronic devices, they are often combined with other cooling solutions for optimal performance. These solutions may include thermal pads, heat pipes, and liquid cooling systems. Each solution has its own advantages and is chosen based on the device's thermal requirements.The Future of Heat Sink TechnologyAs electronic devices continue to evolve, so does heat sink technology. Researchers are constantly exploring new materials and designs to improve heat dissipation and enhance cooling efficiency. Advancements in heat sink technology will contribute to the development of smaller, more powerful, and more energy-efficient electronic devices.Quote Inquiry