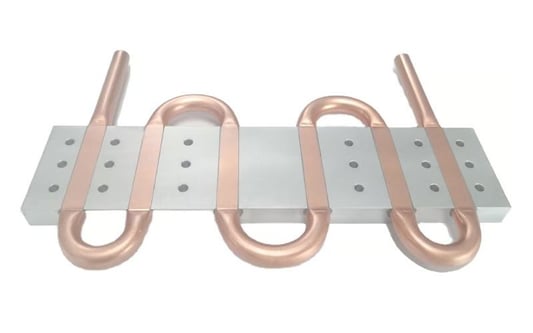
The Basics of liquid cold plate designLiquid cold plate design is a crucial aspect of modern electronic cooling systems. These systems are utilized in electronic devices such as computer servers and industrial machines to manage their temperature and prevent potential damages caused by overheating. Liquid cold plates are the centerpiece of cooling systems, and their design plays a vital role in determining their overall efficiency and effectiveness.The Advantages of Liquid Cold Plate DesignCompared to traditional air-cooled systems, liquid cooling systems such as liquid cold plate design offer several benefits. First and foremost, they can dissipate heat more efficiently, ensuring that the electronic devices do not overheat and damage their components. They are also quieter and require less space compared to air-cooled systems. Additionally, liquid cooling systems can achieve higher cooling power density, meaning they can manage more heat in smaller areas.Factors to Consider when Designing Liquid Cold PlatesSeveral factors must be considered to design an effective and efficient liquid cold plate for electronic cooling systems. These include the materials used, coolant type, flow pattern, and fluid velocity. The design should also ensure that the coolant flows evenly, ensuring equal temperature management across the entire electronic device. The plate's thickness and surface area should also be optimized to maximize heat dissipation while minimizing the overall size of the cooling system.Materials for Liquid Cold Plate DesignThe choice of materials for liquid cold plate design depends on several factors, such as the operating temperature range, pressure, and compatibility with the cooling fluid. Different materials such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium can be used depending on the specific requirements. The materials must also be chosen to prevent any potential corrosion or galvanic reactions that could damage the electronic device.Coolant Selection for Liquid Cold Plate DesignThe right coolant selection is vital to ensure that the liquid cold plate is effective and long-lasting. The coolant must be compatible with the materials used, have the right thermodynamic properties, and offer low environmental impact. Common coolants used include water-glycol solutions, refrigerants, and mineral oils.Flow Pattern and Fluid Velocity in Liquid Cold Plate DesignThe flow pattern and fluid velocity in liquid cold plate design determine how effectively heat is transferred from the electronic components to the coolant. Different flow patterns such as parallel, serpentine, and laminar can be employed depending on the specific design requirements. The fluid velocity should also be optimized for maximum heat dissipation while ensuring that the electronic components are not damaged.The Importance of Simulation in Liquid Cold Plate DesignSimulation is a vital aspect of liquid cold plate design. It allows engineers to model the performance of the cooling system before it is built, enabling early identification of potential issues or inefficiencies. The simulation can also help optimize the design and materials used to ensure maximum performance and efficiency.Testing and Validation of Liquid Cold PlatesOnce the design and simulation are completed, the liquid cold plate design must be tested and validated in real-world conditions. This ensures that the cooling system operates as intended and provides reliable and efficient temperature management. The testing also helps identify any potential issues or inefficiencies that may have been overlooked during the design and simulation process.The Future of Liquid Cold Plate DesignAs electronic devices continue to shrink and become more powerful, liquid cooling systems such as liquid cold plate design will become increasingly important. New materials and technologies are being developed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of liquid cooling systems, allowing them to manage higher heat loads in smaller areas. Future liquid cold plate design applications include electric vehicle batteries and high-performance computing systems.ConclusionLiquid cold plate design is a crucial aspect of modern electronic cooling systems. It plays a vital role in ensuring the reliable and efficient temperature management of electronic devices ranging from computer servers to industrial machines. Through careful consideration of the factors discussed in this article, such as materials selection, coolant choice, flow pattern, and simulation testing, engineers can design highly efficient and effective liquid cold plates for a wide range of applications.Quote InquiryContact us!