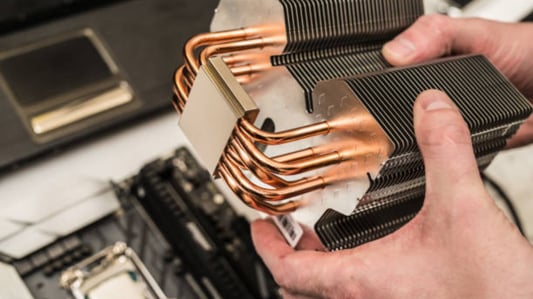
Introduction:When it comes to computer hardware, you may eventually need to perform maintenance or upgrades. One of the most common tasks is replacing a CPU or graphics card heatsink. However, most people are unsure whether thermal pads should be replaced after removing the heatsink. In this article, we'll explore that question and provide you with some useful information.What are Thermal Pads?A thermal pad is a piece of material that is used to transfer heat from a component, such as a CPU or graphics card, to the heatsink. Typically made of silicone or another polymer, thermal pads offer a convenient and mess-free alternative to thermal paste. They are also less likely to lead to a short circuit if excess material gets onto other components.Why Replace Them?If you've removed a heatsink from a CPU or graphics card, you may be wondering why you'd need to replace the thermal pads. The truth is, thermal pads are not designed to be reused. After they have been heated and cooled, they can lose their effectiveness. This can cause your CPU or GPU to run hotter than it should, potentially leading to thermal throttling or component damage over time.How to Tell if They Need Replacing?If you're unsure whether your thermal pads need to be replaced, there are a few signs to watch out for. If you notice that your CPU or GPU temperatures have increased, or if you experience frequent crashes, it could be a sign that your thermal pads are no longer doing their job. Additionally, if you remove the heatsink and notice that the thermal pads have become compressed or discolored, it's a good idea to replace them.How Often?One question that many people have is how often thermal pads should be replaced. The answer depends on several factors, such as how often you use your computer, how hot your components run, and the quality of the thermal pads. As a general rule of thumb, it's a good idea to replace your thermal pads every two to three years if you use your computer frequently.How to Replace Them?If you've determined that your thermal pads need to be replaced, the process is relatively simple. Start by removing the heatsink from your CPU or GPU. Then, carefully remove the old thermal pads from both the component and the heatsink, making sure not to leave any residue behind. Finally, apply a new thermal pad to the component and attach the heatsink. Be sure to follow any manufacturer instructions for the new thermal pad.Can You Use Thermal Paste Instead?Some people may wonder if they can use thermal paste instead of thermal pads. While thermal paste can offer better cooling performance than thermal pads, it can also be messier and more difficult to remove. Additionally, if thermal paste gets onto other components, it could cause a short circuit. It's best to stick with thermal pads, especially if you're unsure about how to work with thermal paste.Benefits of New Thermal PadsIf you're still unsure about whether to replace your thermal pads, there are several benefits to consider. Firstly, new thermal pads can help to keep your CPU or GPU running cooler, which can improve performance and prevent thermal throttling. Additionally, they can help to extend the lifespan of your components by reducing the risk of damage from overheating.ConclusionOverall, if you've removed a heatsink from a CPU or graphics card, it's a good idea to replace the thermal pads. While they may seem like a small component, they play a crucial role in keeping your hardware running cool and preventing damage. By following our advice and paying attention to the signs that your thermal pads need replacing, you'll be able to keep your computer running smoothly for years to come.Quote InquiryContact us!