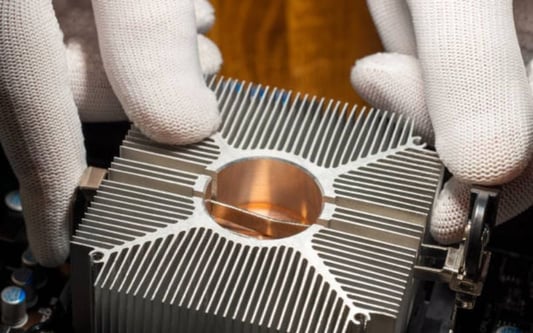
IntroductionWhen building or upgrading your computer, applying thermal paste directly on the processor before installing the heat sink is crucial. Thermal paste fills in microscopic gaps between the processor and heat sink, allowing for better heat transfer and preventing overheating. But What should you apply directly on the processor before installing the heat sink?? In this article, we'll explore the different types of thermal paste and the proper way to apply it.Types of Thermal PasteThere are three main types of thermal paste: ceramic, metal, and silicone. Ceramic paste is non-conductive and ideal for use on sensitive electronics, while metal paste contains small metal particles that help with heat transfer. Silicone paste is a popular choice among computer enthusiasts, as it provides a good balance of performance and ease of use.How Much Thermal Paste to UseWhen applying thermal paste, less is more. Applying too much thermal paste can actually hinder heat transfer, resulting in higher temperatures. A pea-sized amount of thermal paste is all you need. Place it in the middle of the processor, and let the weight of the heat sink spread it evenly.Cleaning the Processor and Heat SinkBefore applying thermal paste, make sure the processor and heat sink are clean. Any dust or debris can hinder heat transfer. Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to clean both surfaces thoroughly.Applying Thermal PasteTo apply thermal paste, follow these simple steps:1. Clean the processor and heat sink.2. Apply a pea-sized amount of thermal paste in the center of the processor.3. Let the weight of the heat sink spread the thermal paste evenly.4. Secure the heat sink in place according to the manufacturer's instructions.Replacing the Heat SinkIf you're replacing the heat sink, be sure to remove any residual thermal paste from the processor and heat sink. Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to clean both surfaces thoroughly before applying new thermal paste and attaching the new heat sink.Choosing the Right Heat SinkIn addition to thermal paste, it's important to choose the right heat sink for your processor. Different processors have different cooling requirements. Be sure to do your research and choose a heat sink that's compatible with your processor.Testing TemperatureAfter applying thermal paste and installing the heat sink, it's a good idea to test the temperature of your processor using a temperature monitoring software. If your processor is running too hot, you may need to reapply thermal paste or invest in a better heat sink.ConclusionApplying thermal paste directly on the processor before installing the heat sink is an essential step in building or upgrading your computer. By choosing the right type of thermal paste, applying it correctly, and choosing the right heat sink, you can ensure your processor stays cool and avoids overheating.thermal paste, processor, heat sink, ceramic paste, metal paste, silicone pasteWhat to Apply on the Processor Before Installing the Heat Sink?Learn what type of thermal paste to apply directly on the processor before installing the heat sink, how much to apply, and other essential tips to keep your processor cool.Quote InquiryContact us!