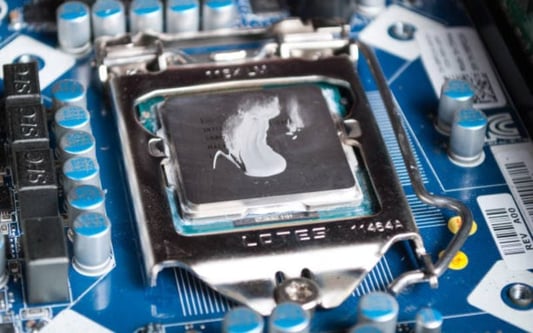
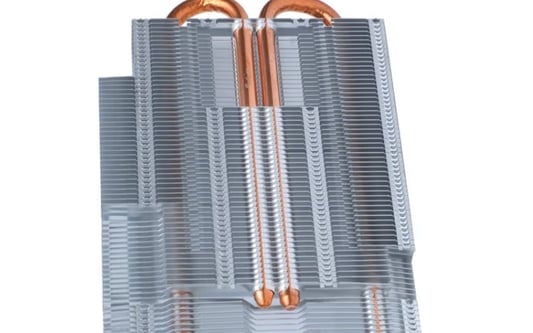
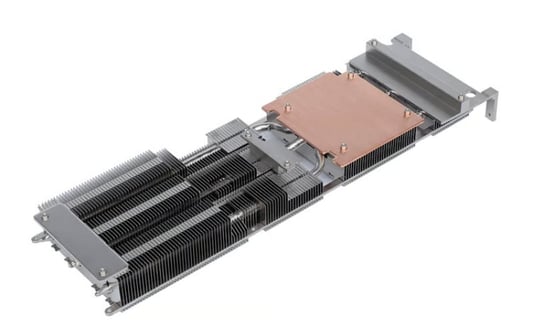
IntroductionWhen it comes to building a high-performance PC, choosing the right CPU cooler can make the difference between smooth operation and overheating. With so many options on the market, how do you know which material is best for your CPU cooler?AluminumAluminum is a popular choice for CPU coolers due to its impressive heat-dissipating properties. The material is lightweight, durable, and relatively inexpensive. However, aluminum is not the most effective at dissipating heat compared to other materials.CopperCopper is another popular choice for CPU coolers. It is a highly conductive material, and its thermal conductivity properties make it the best material to draw heat away from the CPU. Copper is also quite heavy and expensive, but its cooling capabilities make up for its cost.Nickel-Plated CopperNickel-plated copper combines the thermal conductivity of copper with a layer of nickel to prevent oxidation and enhance corrosion resistance. These coolers are a bit more expensive than the regular copper ones, but they provide excellent performance.Direct Contact Heat PipesDirect contact heat pipes are a technology used by some CPU coolers to enhance heat dissipation. They are made of copper and aluminum and are designed to create direct contact between the CPU and the heatsink for more efficient heat transfer.GrapheneGraphene is a relatively new material that is becoming increasingly popular in the realm of cooling. It is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, making it an ideal choice for CPU coolers. Graphene also has a low density, making it a lightweight option for those who prefer to build lightweight PCs. TitaniumTitanium is a highly durable material that is preferred for use in extreme conditions. It is a good thermal conductor and is resistant to corrosion and oxidation. Because of its superior durability and heat dissipation properties, however, titanium is a more expensive option.Thermal PasteThermal paste is not a material per se, but it plays a crucial role in dissipating heat. A small amount of thermal paste is applied between the CPU and the heatsink, allowing maximum surface contact and enhanced heat transfer. The effectiveness of thermal paste depends on its composition and the pressure of the contact between the CPU and heatsink.ConclusionChoosing the right material for your CPU cooler is essential for maintaining optimum performance and preventing overheating. Each material has its pros and cons, so it's crucial to choose one that meets your specific needs and budget.Related long-tail SEO keywords- How different materials affect CPU cooler performance- What are the thermal conductivity properties of different CPU cooler materials?- Best CPU cooler materials for extreme gaming performance CPU cooler, Aluminum, Copper, Nickel-Plated Copper, Direct Contact Heat Pipes, Graphene, Titanium, Thermal Paste, Heat dissipation techniquesWhat material is best for CPU cooler?? A Comprehensive GuideDo you know what material is best for your CPU cooler? Read our comprehensive guide to find out which materials offer the best performance and heat dissipation propertiesQuote InquiryContact us!