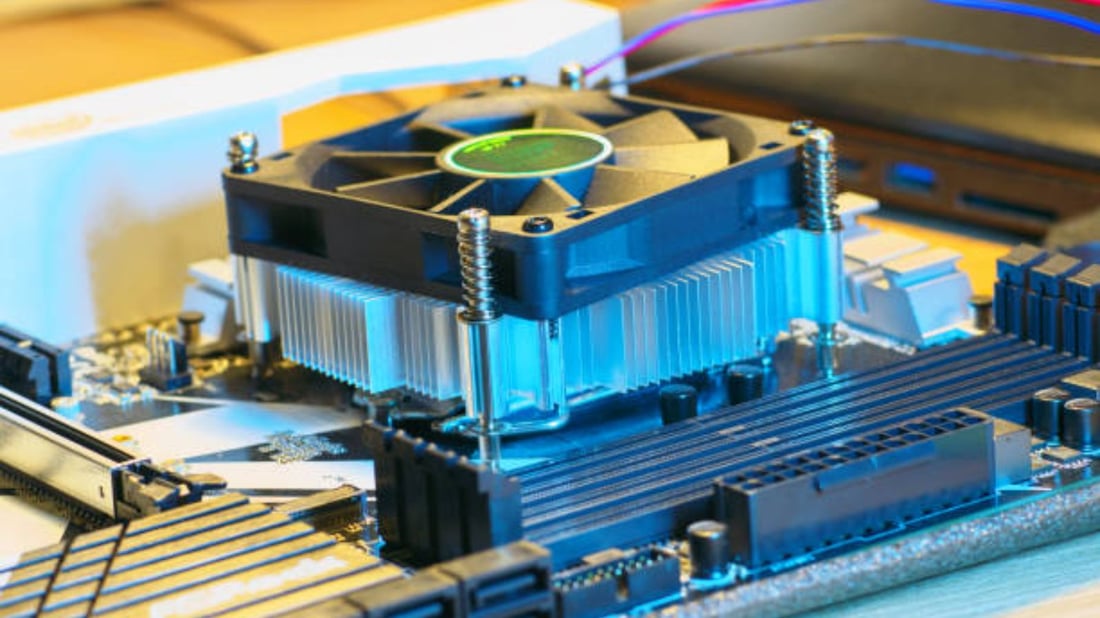
The Importance of Heat Sinks in Electronics
Your electronic devices produce a lot of heat, and that heat can damage the internal components. This is why heat sinks are an essential part of electronics. A heat sink is a passive cooling device that absorbs heat from electronic components and disperses it into the surrounding air. In this article, we’ll discuss how to use a heat sink in electronics to ensure your devices operate at their best.
Choosing the Right Heat Sink
Before you can use a heat sink, you need to choose the right one for your device. The size and shape of your heat sink will depend on the size and power of your electronic component. A larger component will require a larger heat sink to absorb and remove the heat effectively. Choosing the right heat sink is crucial to ensure optimal performance of your device.
Proper Placement of Heat Sinks
Incorrect placement of heat sinks can lead to overheating of electronic components and damaging them. Heat sinks should be placed as close as possible to the heat-producing component to allow for efficient heat transfer. Additionally, heat sinks should have a clear path to move heat away from the component and into the surrounding air.
Types of Heat Sinks
There are several types of heat sinks available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of heat sinks are passive heat sinks, active heat sinks, and liquid-cooled heat sinks. Passive heat sinks are the most common, and they work best in low-power applications. Active heat sinks use a fan to increase airflow and cooling efficiency, while liquid-cooled heat sinks use liquid to transfer the heat away from the components.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Cleaning and maintaining heat sinks is crucial to ensure the optimal performance of your electronic device. Over time, heat sinks can become clogged with dust and debris, reducing their cooling efficiency. Regular cleaning of heat sinks can prevent overheating and improve the longevity of your device.
Thermal Interface Material
Thermal interface material (TIM) is used to improve the thermal conductivity between the electronic component and the heat sink, allowing for more efficient heat transfer. TIMs can be in the form of thermal grease, thermal pads, or phase-change materials. Choosing the right TIM is important to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your electronic device.
Overcoming Challenges of Heat Sinks
While heat sinks are an essential part of electronics, they can also pose challenges. For example, the size and shape of your device may not allow for a traditional heat sink, or the component may produce too much heat for a passive heat sink. In such cases, alternative cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling, can be used.
Understanding Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is a measure of the resistance to heat flow through a material, such as a heat sink. A lower thermal resistance means that the material can transfer heat away from the component more efficiently. Understanding thermal resistance is crucial to choosing the right heat sink for your electronic device.
Cost Considerations
The cost of heat sinks can vary widely depending on the type and size of the sink. For low-power applications, a passive heat sink may be an affordable solution, while high-powered applications may require a more expensive active or liquid-cooled heat sink. Cost considerations should be taken into account when choosing a heat sink.
Conclusion
Heat sinks are an essential part of electronics, absorbing and dissipating the heat produced by electronic components. Proper placement, cleaning, maintenance, and choice of heat sink are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your electronic devices. Understanding thermal resistance and cost considerations are also important factors to consider when choosing a heat sink.
Quote Inquiry
Contact us!