The Importance of Heat Sinks in Electronic Devices
Electronic devices generate a significant amount of heat during operation. This heat can damage the internal components of the device, leading to premature failure. Heat sinks are essential components that help dissipate this heat away from the device. A good heat sink must possess specific properties to ensure optimal heat dissipation and prevent device failure.
High Thermal Conductivity
One essential property of a good heat sink is high thermal conductivity. Heat sinks made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, can effectively transfer heat away from the device. Heat sinks with low thermal conductivity, such as plastics or wood, cannot transfer heat efficiently and are therefore not suitable for use as heat sinks.
Large Surface Area
The surface area of the heat sink also affects its ability to dissipate heat. A larger surface area allows for more efficient cooling because it provides more area for heat to escape. Heat sinks with small surface areas are not as effective and can lead to device failure due to overheating. A good heat sink must, therefore, have a large surface area to maximize heat dissipation.
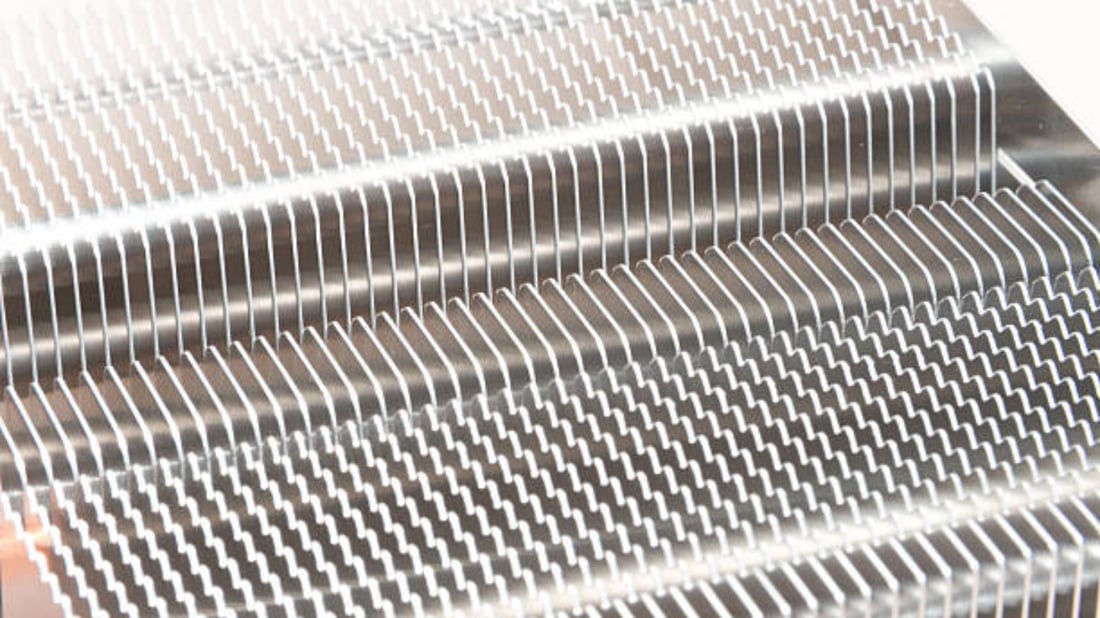
Fin Design
The design of the fins on the heat sink plays a crucial role in its efficiency. Fins with a larger surface area and a higher density can dissipate more heat. A good heat sink should, therefore, have a fin design optimized for maximum heat dissipation. Straight fins, helical fins, and pin fins are examples of fin designs commonly used in heat sinks.
Laminate Material
Lamination of the heat sink material is another critical factor for efficient heat dissipation. Laminated heat sinks have thin layers of highly conductive material stacked together. This design increases the surface area and allows for more efficient heat dissipation. Good heat sinks are, therefore, often made using lamination techniques.
Corrosion Resistance
Heat sinks can be exposed to various environmental conditions that may cause corrosion over time. Corrosion can weaken the heat sink's structure, reducing its capacity to dissipate heat and ultimately leading to device failure. Therefore, a good heat sink must have a high level of corrosion resistance to ensure its longevity and efficient heat dissipation.
Weight
The weight of a heat sink is also a critical factor to consider when selecting one for a particular device. Too heavy a heat sink can put additional stress on the device's internal components, leading to more damage. Heat sinks that are lightweight but still possess the necessary properties for efficient heat dissipation are an excellent choice for use in electronic devices.
Cost
Cost is another critical factor to consider when selecting a heat sink. While heat sinks with the most advanced properties may be the most effective, they are often also the most expensive. Good heat sinks must balance the necessary properties for efficient heat dissipation with cost-effectiveness.
Resistance to Vibration
Electronic devices can generate a significant amount of vibration during operation. Heat sinks that are not designed to withstand device vibration can become detached over time, leading to overheating and device failure. A good heat sink must have a high level of vibration resistance to ensure its longevity and optimal performance.
Compatibility with Electronics System
Each electronic device has unique operating conditions that may affect the performance of the heat sink. A good heat sink must be compatible with the electronics system in which it will be used to ensure optimal heat dissipation. Compatibility issues can lead to device overheating and failure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a good heat sink must have specific properties to ensure optimal heat dissipation and prevent electronic device failure. Properties such as high thermal conductivity, large surface area, optimized fin design, lamination techniques, corrosion resistance, weight, cost-effectiveness, resistance to vibration, and compatibility with electronics systems are crucial for efficient heat dissipation and device longevity.