The Function of Heat Sink: A Comprehensive Guide
Heat sink is an essential component in electronic devices that helps dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or someone curious about the inner workings of electronic devices, understanding the function of heat sink is crucial. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of heat sink and its importance in electronic devices.
1. Understanding Heat Sink
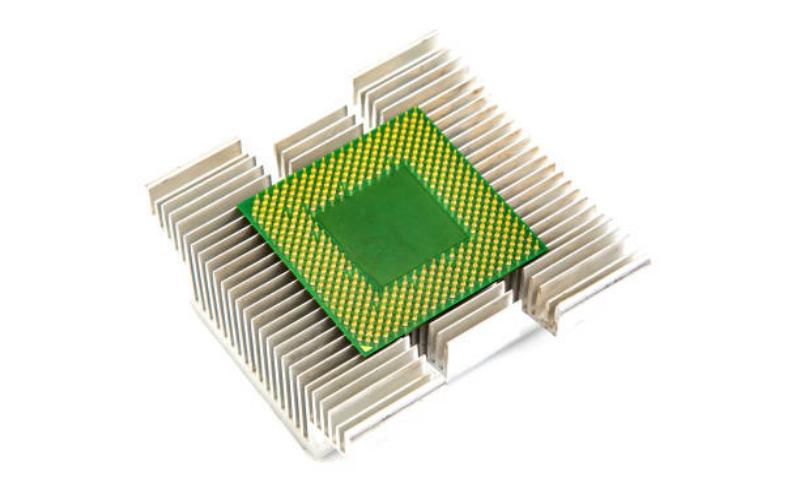
Before delving into its function, let's define what a heat sink is. A heat sink is a passive cooling device that absorbs and dissipates heat generated by electronic components, such as CPUs, GPUs, and power transistors. It typically consists of a metal or alloy material with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. The design of a heat sink involves maximizing its surface area for efficient heat transfer.
2. Heat Transfer Mechanisms
The primary function of a heat sink is to facilitate heat transfer from the electronic component to the surrounding environment. This transfer occurs through three mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the direct transfer of heat between two objects in physical contact. Convection refers to the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid, such as air or liquid. Radiation occurs when heat is emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves.
3. Conductive Heat Transfer
Conductive heat transfer is a vital aspect of a heat sink's function. The heat generated by electronic components is conducted through the base of the heat sink, which is in direct contact with the component. The high thermal conductivity of the heat sink material allows the heat to flow efficiently from the component to the heat sink.
4. Convective Heat Transfer
Convective heat transfer plays a significant role in the function of a heat sink. As the heat is conducted through the heat sink, it needs to be dissipated into the surrounding environment. This is achieved through convective heat transfer, where the heat is transferred to the air or liquid surrounding the heat sink. The design of a heat sink incorporates fins or other structures to increase the surface area and enhance convective heat transfer.
5. Radiative Heat Transfer
In addition to conduction and convection, radiative heat transfer also contributes to the function of a heat sink. Although the contribution of radiation is relatively small compared to conduction and convection, it becomes more significant at higher temperatures. Heat sinks with dark-colored surfaces are designed to emit thermal radiation more effectively.
6. Cooling Performance
The effectiveness of a heat sink in cooling electronic components is determined by its cooling performance. This performance is dependent on several factors, including the material used, the surface area, and the airflow around the heat sink. Heat sinks with larger surface areas and higher thermal conductivity materials tend to have better cooling performance.
7. Importance in Electronic Devices
Heat sinks play a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of electronic devices. Electronic components generate heat during operation, and if not adequately dissipated, it can lead to overheating. Overheating can cause performance degradation, instability, and even permanent damage to the components. Heat sinks help prevent these issues by efficiently dissipating heat and maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
8. Different Types of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications and cooling requirements. Some common types include finned heat sinks, pin heat sinks, and heat pipes. Finned heat sinks have fins that increase the surface area for better convective heat transfer. Pin heat sinks consist of numerous pins that enhance the cooling performance. Heat pipes use a sealed pipe filled with a working fluid to transfer heat more efficiently.
9. Heat Sink Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance of heat sinks are essential to ensure their optimal function. The heat sink should be securely attached to the electronic component using thermal interface materials, such as thermal paste or pads, to maximize heat transfer. Regular cleaning and dust removal from the heat sink's surface are also necessary to maintain its effectiveness in dissipating heat.
10. Advancements in Heat Sink Technology
As technology continues to advance, so does the development of heat sink technology. Engineers and researchers are constantly exploring new materials and designs to improve heat sink performance. Advancements such as liquid cooling systems, phase-change materials, and micro-finned structures are pushing the boundaries of heat sink capabilities.