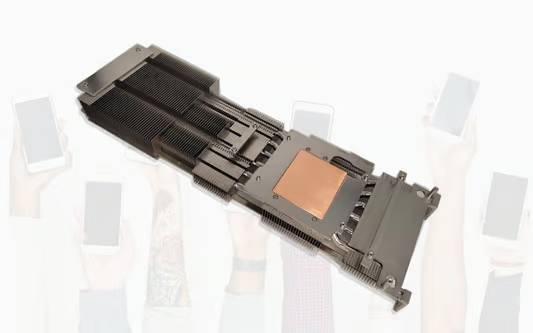
What is the difference between a heat sink and a cold plate?
Heat dissipation is a critical factor in many electronic devices and systems. Two common methods used to manage and control heat are heat sinks and cold plates. While both serve the purpose of cooling components, there are distinct differences between the two in terms of design, functionality, and applications. In this article, we will explore these differences and understand when to use a heat sink or a cold plate.
Heat Sink: Cooling Through Convection
A heat sink is a passive cooling device that helps dissipate heat from electronic components by increasing the surface area available for heat transfer. It is typically made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, with fins or ridges that extend from a base. The primary mode of heat transfer in a heat sink is convection, where heat is transferred from the component to the fins and eventually dissipated into the surrounding air.
Cold Plate: Cooling Through Conduction
A cold plate, on the other hand, is an active cooling device that uses conduction to transfer heat away from electronic components. It consists of a flat metal plate that is in direct contact with the heat source. The plate is often made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum. Cold plates are commonly used in applications where high heat loads need to be efficiently dissipated, such as in power electronics or high-performance computing.
Design and Functionality Differences
Heat sink and cold plate designs differ in terms of their structure and functionality. Heat sinks are designed to maximize the surface area exposed to the surrounding air, allowing for efficient heat dissipation through convection. The fins or ridges on a heat sink increase the surface area, promoting better airflow and heat transfer. Cold plates, on the other hand, are designed for direct contact with the heat source, enabling efficient heat transfer through conduction.
Applications of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks find applications in various electronic devices, including computers, LED lights, power amplifiers, and microprocessors. They are commonly used in situations where passive cooling is sufficient to manage the heat generated by the components. Heat sinks are especially effective in applications where space is limited or when noise from cooling fans needs to be minimized.
Applications of Cold Plates
Cold plates are widely used in industries where high-power electronic components generate substantial amounts of heat that cannot be efficiently managed by traditional cooling methods. They are commonly found in applications such as laser diodes, power electronics, electric vehicle battery cooling, and aerospace systems. Cold plates are particularly effective when heat needs to be quickly transferred away from the source and dissipated through a separate cooling system.
Efficiency and Thermal Performance
The choice between a heat sink and a cold plate depends on the specific cooling requirements of the application. Heat sinks are generally more efficient in dissipating heat when there is sufficient airflow to carry away the heat. On the other hand, cold plates offer higher thermal performance as they provide direct contact between the heat source and the cooling medium, allowing for efficient heat transfer.
Cost Considerations
When it comes to cost, heat sinks are generally more affordable compared to cold plates. The simplicity of their design and ease of manufacturing contribute to their lower cost. Cold plates, on the other hand, require more complex manufacturing processes, such as machining and welding, which can increase their overall cost.
Combining Heat Sinks and Cold Plates
In some cases, a combination of heat sink and cold plate technologies may be employed to achieve optimal cooling performance. This approach is often used in applications where heat is generated in localized areas and needs to be efficiently transferred to a larger cooling system. By combining the strengths of both technologies, it is possible to effectively manage heat in complex electronic systems.
Conclusion
In summary, heat sinks and cold plates are both effective cooling solutions, but they differ in design, functionality, and applications. Heat sinks are passive cooling devices that rely on convection for heat dissipation, while cold plates are active cooling devices that use conduction for efficient heat transfer. The choice between the two depends on factors such as the heat load, available space, airflow conditions, and cost considerations. By understanding the differences between heat sinks and cold plates, engineers and designers can make informed decisions to ensure effective thermal management in their electronic systems.