What does a cold plate do? Everything You Need to Know
A cold plate is a vital component in various industries and applications where efficient cooling is required. It is essentially a heat exchanger that helps dissipate heat from electronic devices, machinery, or even food products. In this article, we will explore the functions and benefits of a cold plate, its different types, and its applications in different industries.
The Function of a Cold Plate
A cold plate works on the principle of thermodynamics and conduction. Its primary function is to transfer heat from a source to a cooling medium, such as air or liquid. By absorbing and dissipating heat, a cold plate helps keep the temperature of the source within acceptable limits, preventing overheating and damage.
Cold plates are typically made of highly conductive materials, such as copper or aluminum, to enhance heat transfer. They often have intricate designs, including fins or tubes, to increase the surface area and improve cooling efficiency.
The Types of Cold Plates
Cold plates come in various types, each designed for specific applications and cooling requirements. The three most common types are:
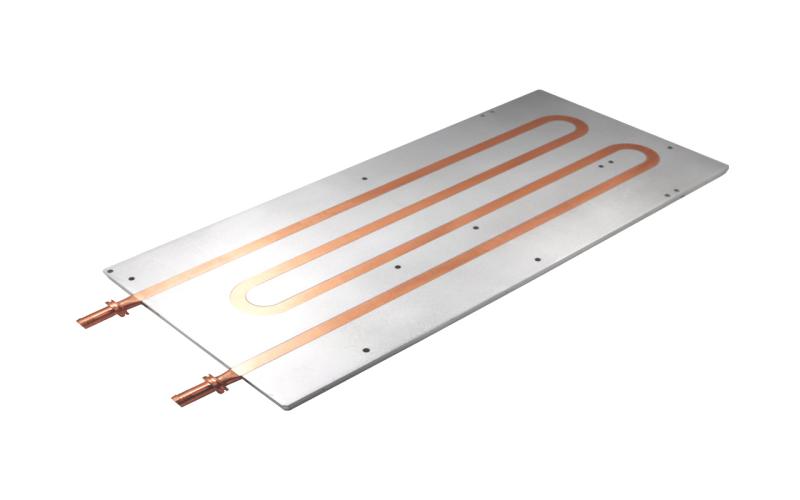
1. Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates utilize a liquid coolant, such as water or a specialized cooling fluid, to transfer heat away from the source. The coolant flows through channels or tubes within the cold plate, absorbing heat as it passes over the hot surface. It then carries the heat away to a heat sink or a separate cooling system.
Liquid cold plates are highly efficient and are commonly used in industries where high-power electronic components or devices generate a significant amount of heat, such as in power electronics, medical equipment, or aerospace applications.
2. Air-Cooled Cold Plates
Air-cooled cold plates, as the name suggests, use forced air to cool the source. They are equipped with fans or blowers that direct airflow over the surface of the cold plate, dissipating heat by convection. Air-cooled cold plates are often used in applications where liquid cooling is not feasible or required.
These types of cold plates are popular in computer cooling systems, LED lighting, telecommunications equipment, and other electronic applications where a moderate cooling solution is sufficient.
3. Hybrid Cold Plates
Hybrid cold plates combine the benefits of both liquid and air cooling. They usually consist of a liquid-cooled base with additional fins or heat pipes for enhanced heat dissipation through natural convection or forced air cooling.
Hybrid cold plates are commonly used in applications that require a higher cooling capacity than air-cooled cold plates but do not require the full capabilities of liquid-cooled solutions. They can be found in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial machinery.
Applications of Cold Plates
Cold plates have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
1. Electronics Cooling
In the electronics industry, cold plates are used to cool high-power components, such as CPUs, GPUs, power amplifiers, and transistors. By efficiently dissipating heat, cold plates help prevent performance degradation and extend the lifespan of electronic devices.
2. Medical Equipment
Cold plates are essential in medical equipment, including MRI machines, laser systems, and laboratory equipment. These devices generate a significant amount of heat that needs to be managed effectively to ensure accurate and reliable operation.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, cold plates are used to maintain the freshness and quality of perishable products. They are employed in refrigeration units, ice cream machines, and cold storage facilities to ensure optimal temperature control and prevent spoilage.
4. Aerospace and Defense
Cold plates play a crucial role in aerospace and defense applications, where electronic systems and avionics need to operate in extreme environments. They are used to cool critical components in radar systems, satellites, avionics racks, and military vehicles.
5. Energy and Power Systems
Cold plates are utilized in energy and power systems, such as electric vehicles, solar inverters, and wind turbines. They help dissipate heat generated by power electronics, enhance system efficiency, and ensure reliable operation.
Conclusion
In summary, a cold plate is a highly efficient heat exchanger that plays a crucial role in various industries and applications. Whether it's cooling electronic components, medical equipment, or food products, cold plates help maintain optimal temperatures and prevent overheating. By understanding the different types of cold plates and their applications, industries can make informed decisions to improve performance, reliability, and overall efficiency.