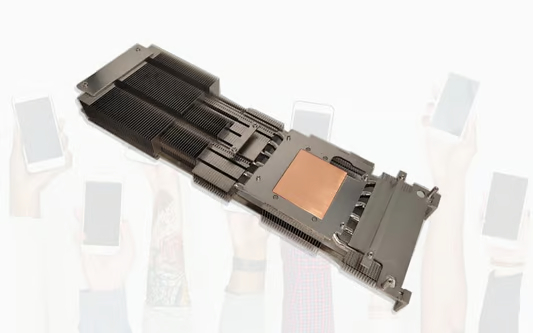
Is thicker heatsink better?
When it comes to computer hardware, one component that often gets overlooked but plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance is the heatsink. The heatsink is responsible for dissipating the heat generated by the CPU or GPU, preventing overheating and potential damage. But is thicker always better when it comes to heatsinks? In this article, we will explore the various aspects of heatsinks and determine whether a thicker heatsink truly leads to better heat dissipation.
The Importance of Heat Dissipation
Before delving into the thickness of heatsinks, it is essential to understand why heat dissipation is crucial. Modern CPUs and GPUs generate a significant amount of heat during operation, and without proper cooling, this heat can accumulate and cause the components to overheat. Overheating can lead to a decrease in performance, system instability, and even permanent damage. The primary purpose of a heatsink is to draw heat away from the component and dissipate it into the surrounding environment.
Understanding Heatsink Design
Heatsinks are typically made of metal, such as aluminum or copper, due to their excellent thermal conductivity properties. The design of a heatsink consists of numerous fins or ridges that increase the surface area available for heat dissipation. The larger the surface area, the more efficiently the heatsink can transfer heat to the surrounding air. However, the thickness of the heatsink also plays a role in its overall performance.
Thicker Heatsink: More Mass, More Heat Capacity
One advantage of a thicker heatsink is its increased mass, which allows it to absorb and store more heat. By having a greater heat capacity, a thicker heatsink can handle higher heat loads without becoming overwhelmed. This can be particularly beneficial when dealing with intense workloads or overclocking scenarios where the component is pushed to its limits. The additional mass of a thicker heatsink can help prevent thermal throttling and maintain stable performance.
Optimal Fin Spacing and Airflow
While a thicker heatsink may offer advantages in terms of heat capacity, it is crucial to consider other factors that affect heat dissipation, such as fin spacing and airflow. The spacing between the fins of a heatsink determines how efficiently it can transfer heat to the surrounding air. Too much spacing can reduce the effectiveness of the heatsink, while too little spacing can hinder airflow and lead to inadequate cooling.
The Role of Airflow
Airflow is essential for efficient heat dissipation, as it carries away the heat from the heatsink. Thicker heatsinks may require more airflow to ensure that heat is effectively removed. This can be achieved through the use of additional fans or by optimizing the overall airflow within the computer case. It is important to strike a balance between the thickness of the heatsink and the available airflow to achieve optimal cooling performance.
Real-World Performance Considerations
When considering whether a thicker heatsink is better, it is essential to take into account real-world performance scenarios. In many cases, the stock heatsink provided with CPUs or GPUs is designed to meet the recommended thermal specifications under normal operating conditions. Upgrading to a thicker heatsink may not yield significant improvements unless the system is subjected to heavy workloads or overclocking.
Other Factors Affecting Heat Dissipation
While the thickness of a heatsink is an important consideration, it is not the sole factor that determines its effectiveness. Other aspects, such as the quality of the thermal interface material between the component and the heatsink, the efficiency of the fan(s) used for cooling, and the overall ventilation within the system, also play a significant role in heat dissipation. These factors should not be overlooked when aiming for optimal cooling performance.
Customization and Aftermarket Solutions
For enthusiasts and users seeking maximum cooling performance, aftermarket heatsinks and cooling solutions are available. These solutions often provide thicker heatsinks with enhanced design features, such as heat pipes or additional fan mounts. When considering aftermarket solutions, it is essential to research and choose a heatsink that is compatible with the specific CPU or GPU and consider the overall thermal requirements of the system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the thickness of a heatsink is just one aspect to consider when aiming for efficient heat dissipation. While a thicker heatsink can offer advantages in terms of heat capacity, it is essential to balance this with proper fin spacing, airflow, and other factors that affect cooling performance. In most cases, the stock heatsink provided with the component is designed to meet the thermal requirements under normal operating conditions. However, for those pushing their systems to the limits or seeking maximum cooling performance, upgrading to a thicker heatsink or exploring aftermarket solutions can be beneficial.