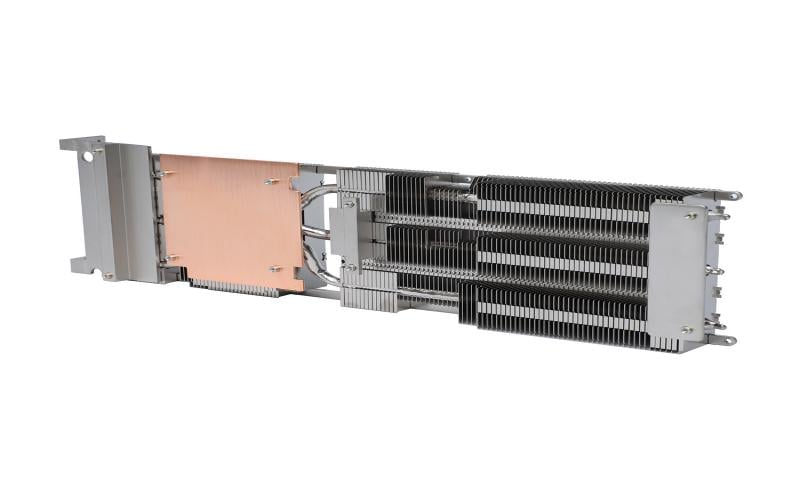
The Manufacturing Process of Heat Sinks
Introduction: Heat sinks play a crucial role in cooling electronic devices, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. But have you ever wondered how these essential components are manufactured? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the heat sink manufacturing process, exploring each step involved.
1. Design and Material Selection
Before the manufacturing process begins, heat sink manufacturers must first design the product. This involves considering the specific requirements of the application, such as the power dissipation, size constraints, and thermal resistance. Once the design is finalized, the appropriate materials are selected, typically aluminum or copper due to their excellent thermal conductivity.
2. Extrusion
Extrusion is the most common manufacturing method for heat sinks. The process starts with an aluminum or copper billet, which is heated and pushed through a die using a hydraulic press. This results in the desired shape and size of the heat sink. The extruded heat sink is then cut into the required length and undergoes further machining to create fins and other features.
3. Die Casting
Die casting is another popular method for manufacturing heat sinks, especially when intricate designs or complex geometries are required. In this process, molten metal is injected into a die under high pressure. Once cooled and solidified, the heat sink is removed from the die and undergoes secondary operations like trimming and surface finishing.
4. Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process that involves shaping metal by applying compressive force. While it is less commonly used for heat sink production, it can be employed for specific applications requiring high strength and durability. The forging process enhances the mechanical properties of the heat sink, making it suitable for demanding environments.
5. CNC Machining
Once the heat sink has been extruded, die-cast, or forged, it undergoes CNC machining to refine its shape and dimensions. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines use pre-programmed computer software to precisely remove material from the heat sink and create intricate features like fins, mounting holes, and grooves. This step ensures the heat sink meets the exact specifications of the design.
6. Surface Treatment
Surface treatment is essential for heat sinks to improve their performance and protect against corrosion. Anodization is the most common surface treatment method, where the heat sink is immersed in an electrolyte bath and subjected to an electric current. This process forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, increasing durability and enhancing thermal performance.
7. Finishing Touches: Coating and Painting
Depending on the application and aesthetic requirements, heat sinks may undergo additional finishing touches. Coatings such as epoxy or silicone can be applied to improve electrical insulation or provide a protective layer. Heat sinks can also be painted to match specific color schemes or branding requirements.
8. Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure the heat sinks meet the required standards. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspection, and thermal performance testing. Quality control is crucial to guarantee the reliability and effectiveness of the heat sinks in real-world applications.
9. Packaging and Distribution
After passing the quality control tests, the heat sinks are carefully packaged to prevent any damage during transportation. They are then distributed to various industries, including electronics, automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications. The packaging process involves protecting the heat sinks from moisture, dust, and other potential contaminants.
10. Continuous Improvement
Heat sink manufacturing is a constantly evolving field, and manufacturers strive for continuous improvement in their processes. By investing in research and development, adopting advanced technologies, and incorporating customer feedback, heat sink manufacturers ensure they stay at the forefront of innovation, delivering heat sinks that meet the ever-increasing demands of modern electronic devices.