Understanding the Cooling Mechanisms of Electronic Devices
Electronic devices have become an integral part of our lives, serving various purposes ranging from communication to entertainment. However, these devices generate a significant amount of heat while in operation, which can lead to performance issues and even permanent damage. To prevent this, electronic devices are equipped with cooling mechanisms that dissipate heat efficiently. In this article, we will explore the different methods used to cool electronic devices and how they work.
1. Passive Cooling: The Basics
Passive cooling is the simplest and most common method used to cool electronic devices. It relies on natural heat dissipation mechanisms without the need for any additional components. Heat is transferred from the device to the surrounding environment through conduction, convection, and radiation. Passive cooling is often utilized in devices with low power consumption, such as smartphones and tablets.
2. Active Cooling: Introducing Fans and Heat Sinks
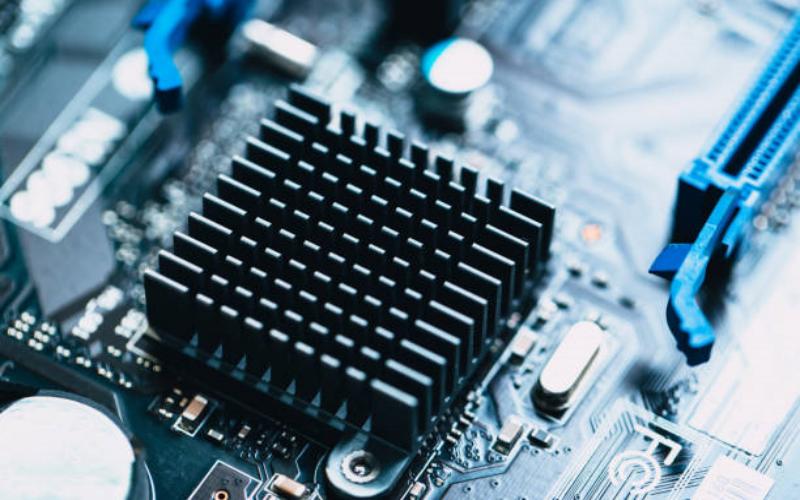
For electronic devices with higher power requirements, active cooling methods are employed to enhance heat dissipation. This involves the use of fans and heat sinks, which actively remove heat from the device. The fan circulates air around the device, while the heat sink absorbs and dissipates the heat generated. This combination is commonly seen in desktop computers and gaming consoles.
3. Liquid Cooling: Taking Efficiency to the Next Level
Liquid cooling is a more advanced method used to cool high-performance electronic devices, such as servers and high-end gaming systems. It involves circulating a liquid coolant through a closed loop system, which absorbs and carries away the heat. Liquid cooling offers higher efficiency and allows for more precise temperature control compared to air cooling methods.
4. Thermoelectric Cooling: Harnessing the Peltier Effect
Thermoelectric cooling utilizes the Peltier effect to cool electronic devices. It involves the use of thermoelectric modules that consist of two dissimilar conductive materials. When an electric current is passed through the module, one side becomes cooler while the other side becomes hotter. This technology is commonly found in portable refrigerators and some high-performance laptops.
5. Phase-Change Cooling: From Liquid to Gas
Phase-change cooling is a specialized cooling method used in extreme-performance electronic devices, such as overclocked processors and graphic cards. It utilizes the principle of phase change, where a liquid coolant rapidly evaporates upon contact with a hot surface, absorbing a significant amount of heat in the process. This vapor then condenses back into a liquid, ready to repeat the cycle.
6. Heat Pipes: Efficient Heat Transfer at its Best
Heat pipes are highly efficient heat transfer devices commonly used in laptops and smartphones. They consist of a sealed copper pipe filled with a small amount of working fluid. When heat is applied to one end of the pipe, the fluid evaporates and travels to the other end, where it condenses and releases the absorbed heat. Heat pipes provide a compact and effective cooling solution.
7. Graphene-based Cooling: The Future of Electronics Cooling
Graphene, a revolutionary material known for its excellent thermal conductivity, holds immense potential in the field of electronic device cooling. Researchers are exploring the use of graphene-based heat spreaders and thermal interface materials to enhance heat dissipation and improve overall device performance. Although still in the experimental stage, graphene-based cooling shows promising results.
8. Active Heat Management: Intelligent Cooling Solutions
Modern electronic devices often incorporate active heat management systems that utilize sensors and intelligent algorithms to dynamically adjust cooling mechanisms. These systems monitor temperature levels and adjust fan speeds, coolant flow rates, and other parameters to ensure optimal cooling under varying load conditions. Active heat management improves efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of electronic devices.
9. Environmental Considerations: Cooling and Sustainability
As the demand for electronic devices continues to rise, so does the need for sustainable cooling solutions. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing energy-efficient cooling mechanisms and materials that minimize environmental impact. This includes the use of eco-friendly cooling fluids, recyclable components, and designs that promote efficient heat dissipation.
10. Future Trends: Cooling for Next-Generation Devices
With the rapid advancement of technology, the cooling requirements of next-generation electronic devices are expected to increase. Researchers are exploring innovative cooling techniques such as carbon nanotubes, advanced microfluidics, and even bio-inspired cooling systems. These developments aim to address the challenges posed by ever-evolving electronic devices and ensure their optimal performance and longevity.