What's the Best Material for Heatsinks? Exploring the Top Choices
Heatsinks are essential components in electronic devices, helping to dissipate heat and prevent overheating. While the design and size of heatsinks play a crucial role, the choice of material is equally important. In this article, we will explore the top materials used for heatsinks, their properties, and their suitability for different applications.
1. Aluminum Heatsinks: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials for heatsinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity and cost-effectiveness. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as laptops and mobile devices. Additionally, aluminum heatsinks are easily manufactured and can be customized to fit various shapes.
2. Copper Heatsinks: Superior Thermal Conductivity
When it comes to thermal conductivity, copper is unmatched. It has nearly twice the thermal conductivity of aluminum, making it highly efficient at transferring heat away from electronic components. Copper heatsinks are commonly used in high-performance applications, such as gaming computers and power electronics, where heat dissipation is critical.
3. Graphite Heatsinks: Lightweight and Versatile
Graphite heatsinks have gained popularity in recent years due to their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight nature. They are particularly useful for applications that require high thermal performance in a limited space. Graphite heatsinks are commonly found in LED lighting, power modules, and other compact electronic devices.
4. Ceramic Heatsinks: High Thermal Stability
Ceramic heatsinks offer exceptional thermal stability, making them suitable for applications that require high operating temperatures. They can withstand extreme heat and provide reliable thermal management in demanding environments. Ceramic heatsinks are commonly used in industrial equipment, power electronics, and automotive applications.
5. Thermal Compound: Enhancing Heat Transfer
While not a material for heatsinks themselves, thermal compounds play a vital role in optimizing heat transfer between the heatsink and the electronic components. These compounds, often made from silicone or ceramic materials, fill in microscopic gaps and imperfections, improving thermal conductivity. Using a high-quality thermal compound can significantly enhance the overall performance of a heatsink.
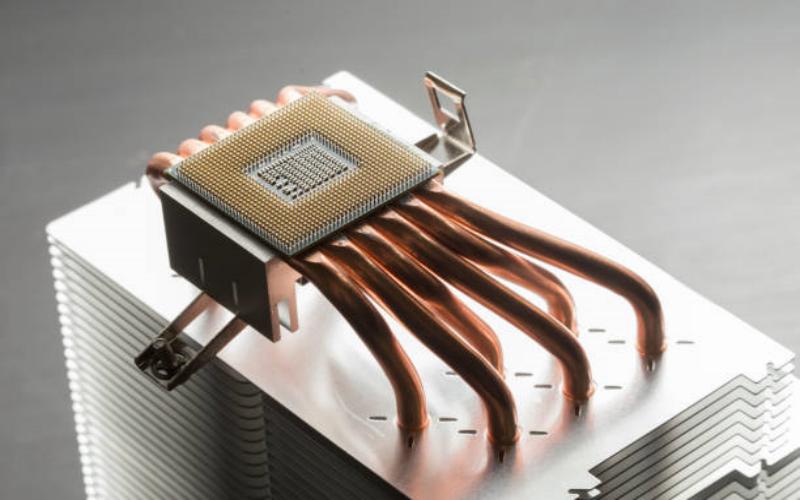
6. Heat Pipes: Efficient Heat Transfer
Heat pipes are another component used in conjunction with heatsinks to improve heat dissipation. They are typically made of copper or aluminum and contain a small amount of fluid. Heat pipes work by transferring heat from the source to the heatsink through phase change principles, ensuring efficient heat transfer over longer distances. They are commonly found in high-performance desktop computers and servers.
7. Vapor Chamber Heatsinks: Advanced Cooling Technology
Vapor chamber heatsinks represent a more advanced cooling solution, especially for high-power applications. These heatsinks consist of a sealed chamber containing a small amount of fluid. The fluid evaporates at the heat source, travels to the cooler regions, condenses, and then returns to the heat source. Vapor chamber heatsinks offer excellent thermal conductivity and are commonly used in graphics cards and high-end processors.
8. Aluminum Alloy Heatsinks: Strength and Thermal Efficiency
Aluminum alloys, which are a combination of aluminum and other elements, offer improved strength and thermal efficiency compared to pure aluminum heatsinks. These alloys can be tailored to specific requirements, providing better mechanical stability and allowing for effective heat dissipation. Aluminum alloy heatsinks find applications in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
9. Beryllium Copper Heatsinks: High Heat Resistance
Beryllium copper heatsinks are known for their exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand high operating temperatures. These heatsinks are commonly used in telecommunications, computer networking, and high-frequency electronic devices.
10. Liquid Cooling Systems: Ultimate Thermal Management
While not a material, liquid cooling systems deserve a mention as they provide the highest level of thermal management. These systems use a liquid coolant, such as water or specialized fluids, to absorb heat from electronic components. The liquid then circulates through a radiator or other cooling components, dissipating the heat into the surrounding environment. Liquid cooling systems are commonly employed in high-performance gaming PCs, server farms, and overclocked systems.