The Difference Between Skived and Extruded Heat Sinks
Heat sinks play a crucial role in thermal management, dissipating heat generated by electronic components. Two popular types of heat sinks are skived and extruded heat sinks. While both serve the same purpose, they have distinct differences in their manufacturing processes and performance characteristics. In this article, we will explore the dissimilarities between skived and extruded heat sinks, and discuss their advantages and disadvantages in various applications.
Skived Heat Sinks
Skived heat sinks are manufactured by a process known as skiving, which involves slicing thin sheets of metal from a solid block. The material used for skived heat sinks is typically copper or aluminum due to their excellent thermal conductivity. Skiving is performed using a specialized machine equipped with a custom-designed blade that cuts the metal sheets in a continuous spiral pattern.
Skived heat sinks offer several advantages. Firstly, their thin fins allow for efficient heat transfer and dissipation, making them suitable for applications with limited space. The skiving process also allows for intricate fin designs, maximizing the surface area and optimizing cooling performance. Additionally, skived heat sinks have a smooth surface finish, which enhances their aesthetic appeal and facilitates better contact with the heat source.
However, skived heat sinks also have some limitations. The manufacturing process is time-consuming and requires specialized equipment, which can increase production costs. Furthermore, the thin fins of skived heat sinks are more susceptible to damage from handling and vibration. Therefore, they are commonly used in applications where space is a constraint, and high cooling performance is essential, such as in laptops, LED lighting, and power electronics.
Extruded Heat Sinks
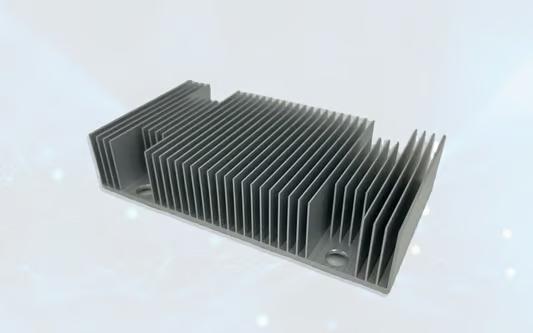
Extruded heat sinks are created through an extrusion process, which involves forcing heated aluminum or copper alloy through a specially designed die. The die shapes the metal into the desired heat sink profile, including fins and base. Extruded heat sinks are available in various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different cooling requirements.
One of the major advantages of extruded heat sinks is their cost-effectiveness. The extrusion process allows for mass production, reducing manufacturing costs compared to other methods. Additionally, the fins of extruded heat sinks are generally thicker and sturdier than those of skived heat sinks, making them more resistant to damage and vibration. The larger surface area provided by the fins ensures efficient heat dissipation, even in applications with moderate airflow.
However, due to the extrusion process, the fins of these heat sinks have a less complex design and limited surface area compared to skived heat sinks. This can result in slightly lower cooling performance in applications where space is less restricted or higher cooling efficiency is required. Extruded heat sinks are commonly used in applications such as power amplifiers, audio equipment, and industrial machinery.
Conclusion
In summary, skived and extruded heat sinks differ in their manufacturing processes, performance characteristics, and applications. Skived heat sinks offer excellent cooling performance in limited spaces but are more vulnerable to damage. On the other hand, extruded heat sinks are cost-effective, sturdy, and suitable for applications with moderate cooling requirements.
When selecting a heat sink, it is essential to consider the specific cooling needs, available space, budget, and desired performance. Consulting with an expert in thermal management can help determine the most suitable type of heat sink for your application, ensuring optimal heat dissipation and reliability.