Introduction
Extruded heatsinks are an important component of electronic devices that help dissipate heat generated during their operation. In this article, we will explore what extruded heatsinks are, how they work, their types, and their applications.
What is extruded heatsink??
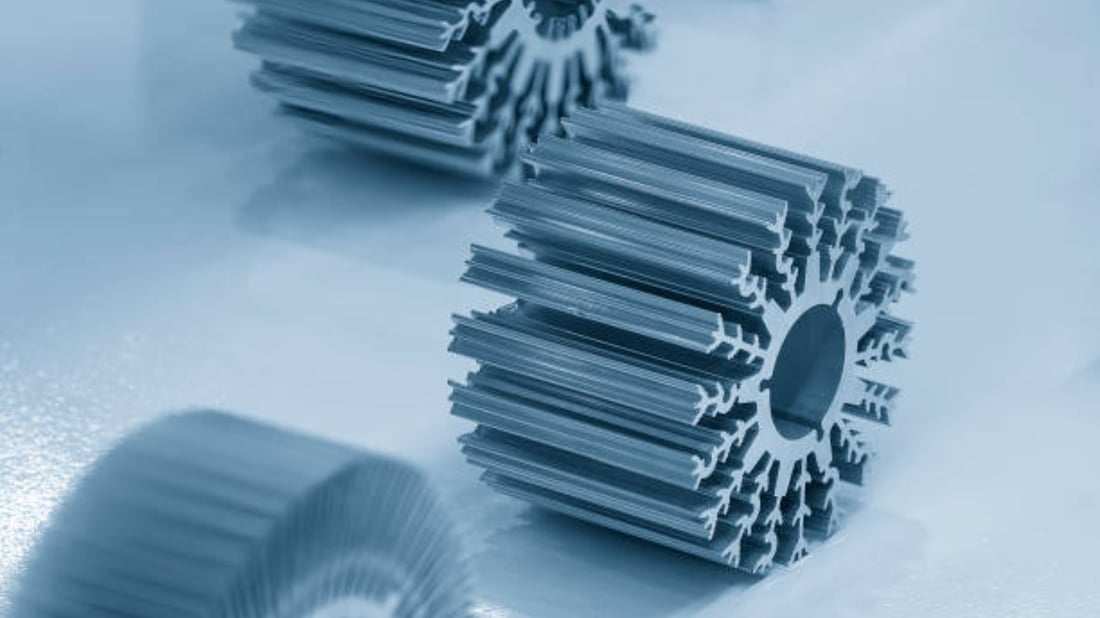
Extruded heatsinks are metal cooling devices used to dissipate excess heat generated by electronic components, such as CPUs, GPUs, and power transistors. They are made using extrusion manufacturing process by forcing heated aluminum or other metals through a die, which gives them a unique shape and design.
Working Principle of Extruded Heatsink
Extruded heatsinks work on the principle of conduction and convection. When the electronic component generates heat, it is transferred to the heatsink through conduction. The heatsink then dissipates the heat through convection, which involves the movement of air and the transfer of heat to it. The larger the surface area of a heatsink, the more effectively it can dissipate heat, which is why extruded heatsinks have fins or grooves on their surface.
Types of Extruded Heatsink
There are three types of extruded heatsinks: passive, active, and custom. Passive heatsinks do not require any external power source and rely solely on convection to dissipate heat. Active heatsinks, on the other hand, use fans or other pressure systems to improve airflow and heat dissipation. Custom heatsinks are designed to meet specific requirements of the electronic device, such as shape, size, and material.
Advantages of Extruded Heatsinks
Extruded heatsinks offer several advantages over traditional cooling methods, such as water cooling and air cooling. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to manufacture. They also have a high thermal conductivity, which means they can transfer heat efficiently. Additionally, they can be customized to match the shape and size of the electronic component, which minimizes the need for additional space or modifications.
Applications of Extruded Heatsink
Extruded heatsinks are used in a wide range of electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, power supplies, LED lights, audio amplifiers, and automotive electronics. They are especially useful in applications where high thermal dissipation is required, such as gaming systems and industrial automation equipment. Extruded heatsinks are also commonly used in the aerospace industry, where lightweight and efficient cooling solutions are crucial.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Extruded Heatsinks
When choosing an extruded heatsink for your electronic device, there are several factors to consider. These include thermal performance, airflow, noise level, size, weight, material, and cost. It is important to balance these factors to ensure that the heatsink meets the specific needs of your device while staying within the budget.
How to Install Extruded Heatsink?
Installing extruded heatsinks is a straightforward process. First, clean the surface of the electronic component thoroughly to remove any dust or debris. Then apply thermal paste to the surface to minimize air gaps and improve heat transfer. Next, place the heatsink on top of the component, making sure that it is aligned properly. Finally, secure the heatsink in place using screws or other fasteners.
Maintenance of Extruded Heatsinks
Maintaining extruded heatsinks is important to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Regular cleaning of the heatsink and fan using compressed air and cloth is recommended to remove any dust or debris that may accumulate on the surface. It is also important to monitor the temperature of the electronic component to ensure that it is not overheating, which can damage the device and reduce its lifespan.
Conclusion
Extruded heatsinks are an essential component of electronic devices that require efficient cooling solutions. They are made using extrusion manufacturing process, come in various types and designs, and offer several advantages over traditional cooling methods. By understanding the principles of extruded heatsinks, their applications, and factors to consider when choosing them, you can make informed decisions about how to optimize the cooling performance of your electronic devices.