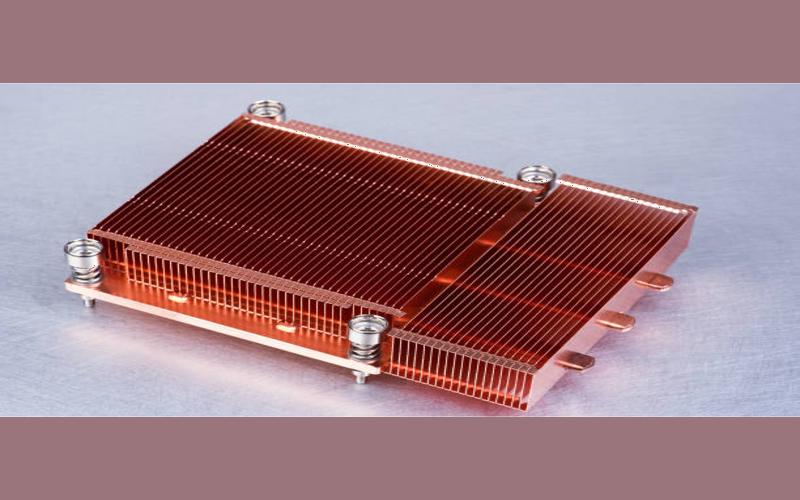
The Importance of Heat Sinks: Understanding Their Functions and Uses
Heat sinks play a vital role in various electronic devices, helping to dissipate excessive heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures. From computers and smartphones to automobiles and industrial machinery, heat sinks are essential components that ensure the longevity and efficiency of electronic systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of heat sinks, exploring their functions, uses, and significance in different applications.
1. Enhancing Thermal Management
One of the primary purposes of a heat sink is to enhance thermal management in electronic devices. As electronic components generate heat during operation, a heat sink acts as a passive cooling mechanism that helps to dissipate this heat. By effectively transferring heat away from the heat-generating components, a heat sink prevents overheating and potential damage.
2. Increasing the Surface Area
Heat sinks are designed with numerous fins or ridges, which significantly increase the surface area available for heat dissipation. These fins provide additional pathways for heat to escape into the surrounding environment, allowing for efficient cooling. The greater the surface area of a heat sink, the more effective it is at dissipating heat.
3. Facilitating Convection of Heat Sinks
Convection is a crucial mechanism for heat transfer and plays a prominent role in heat sink operation. As the heat sink absorbs heat from the electronic component, surrounding air particles get heated, becoming less dense and rising. This creates a convection current that helps transport the heat away, further aiding in the dissipation process.
4. Improving Heat Transfer through Thermal Interfaces
Heat sinks are typically attached to the heat-generating components through a thermal interface material, such as thermal paste or adhesive pads. These interfaces help to fill any gaps between the heat sink and the component, ensuring efficient heat transfer. By minimizing the thermal resistance at the interface, the heat sink can maximize heat dissipation.
5. Cooling CPUs and GPUs
One of the most common applications of heat sinks is in cooling central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs) in computers. These high-performance components generate substantial amounts of heat, which can degrade their performance or even cause permanent damage if not adequately controlled. Heat sinks, often combined with cooling fans, help maintain optimal temperatures and prevent thermal throttling.
6. Enhancing LED Efficiency of Heat Sinks
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are widely used in various lighting applications. However, they can also generate significant amounts of heat, which can negatively impact their performance and lifespan. Heat sinks designed specifically for LEDs help dissipate the heat produced, ensuring the LEDs operate efficiently and maintain their brightness and color accuracy over time.
7. Cooling Power Electronic Devices of Heat Sinks
Power electronic devices, such as inverters and motor drives, are commonly used in industrial applications. These devices handle high currents and voltages, resulting in substantial heat generation. Heat sinks play a critical role in cooling these power electronic components, preventing performance degradation, and ensuring their reliability and longevity.
8. Thermal Management in Automotive Applications
In modern automobiles, numerous electronic systems and components are susceptible to heat-related issues. Heat sinks are employed in automotive applications to manage the heat generated by various components, including engine control units (ECUs), power modules, and LED headlights. Effective thermal management in vehicles helps improve performance, reliability, and overall safety.
9. Industrial Machinery and Heat Dissipation
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment and heavy-duty machinery, often operates in demanding environments and handles high power loads. Heat sinks are vital in these applications for dissipating the significant amount of heat generated during operation. Efficient heat dissipation helps maintain the performance and reliability of the machinery, reducing the risk of breakdowns and costly downtime.
10. Importance in Aerospace and Military Electronics
In aerospace and military applications, electronic devices face extreme conditions, including high temperatures and vibrations. Heat sinks are indispensable in these environments, ensuring that sensitive electronic components remain within safe operating temperatures. By dissipating heat effectively, heat sinks contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of aerospace and military electronics.