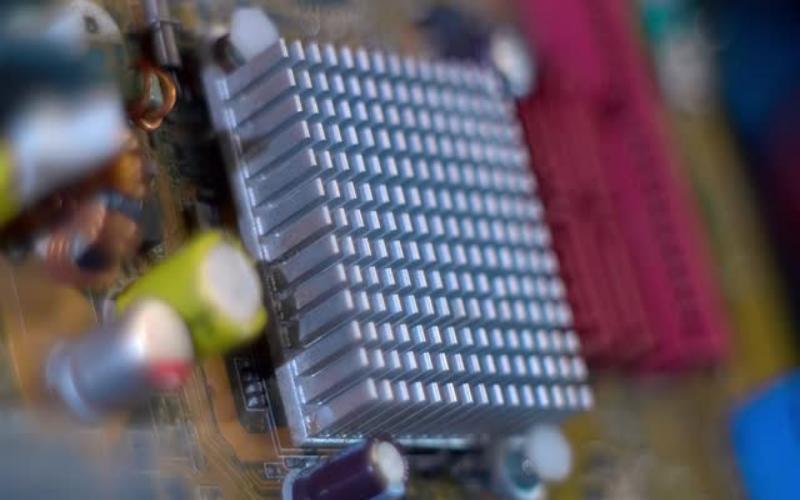
The Importance of Heat Sinks in Electronics
Heat sinks play a vital role in managing the temperature of electronic devices, ensuring their optimal performance and preventing damage caused by overheating. By dissipating heat away from components, heat sinks help maintain the longevity and reliability of electronics. In this article, we will explore the different types of heat sinks commonly used in various applications.
1. Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks are the most common type and are widely used in electronic devices. These heat sinks rely on natural convection to transfer heat away from components. They are typically made of aluminum or copper, which have excellent thermal conductivity. Passive heat sinks are often equipped with fins, which increase the surface area for better heat dissipation.
2. Active Heat Sinks
Active heat sinks, also known as fan-cooled heat sinks, incorporate a fan to enhance the cooling process. The fan helps to increase airflow and improve heat dissipation by blowing air over the heat sink's fins. Active heat sinks are ideal for applications where passive cooling is insufficient, such as high-performance CPUs and graphics cards.
3. Liquid Heat Sinks
Liquid heat sinks utilize liquid, such as water or coolant, to transfer heat away from components. These heat sinks consist of tubes or channels through which the liquid flows, absorbing heat from the electronics. Liquid heat sinks are highly efficient and are commonly used in high-power applications, such as servers and power amplifiers.
4. Thermoelectric Heat Sinks
Thermoelectric heat sinks employ the Peltier effect to cool electronic devices. They consist of thermoelectric modules that create a temperature gradient when an electric current passes through them. One side of the module absorbs heat, while the other side dissipates it. Thermoelectric heat sinks are compact and find applications in miniaturized electronic devices.
5. Bonded Fin Heat Sinks
Bonded fin heat sinks are designed for applications with limited space. These heat sinks consist of a base plate with multiple fins attached directly to it. The fins are bonded to the base plate using methods like epoxy or soldering. Bonded fin heat sinks provide excellent thermal performance in compact electronic devices.
6. Extruded Heat Sinks
Extruded heat sinks are mass-produced heat sinks made by extruding aluminum or copper. They have a simple design and are cost-effective. Extruded heat sinks often have fins that run along the length of the heat sink, providing ample surface area for heat dissipation. These heat sinks are commonly used in consumer electronics and LED lighting applications.
7. Stacked Fin Heat Sinks
Stacked fin heat sinks are designed to maximize heat dissipation in applications with limited space. These heat sinks consist of multiple thin fins stacked on top of each other, creating a larger surface area within a compact form factor. Stacked fin heat sinks are commonly used in laptop computers and compact electronic devices.
8. Plate Fin Heat Sinks
Plate fin heat sinks feature a flat base plate with fins extending vertically from it. These heat sinks provide efficient cooling in applications with moderate airflow. The fins are closely spaced to optimize heat transfer, and the large surface area allows for effective dissipation. Plate fin heat sinks are commonly used in power supplies and audio amplifiers.
9. Pin Fin Heat Sinks
Pin fin heat sinks have a unique design consisting of multiple cylindrical pins extending vertically from a base plate. These pins increase the heat sink's surface area and promote better airflow. Pin fin heat sinks are effective in applications where space is limited and airflow is restricted, such as in compact electronic enclosures.
10. Folded Fin Heat Sinks
Folded fin heat sinks feature a folded or zigzag fin pattern, providing a larger surface area for heat dissipation. This design allows for efficient cooling in applications with low airflow. Folded fin heat sinks are commonly used in aerospace and automotive electronics, where space is limited, and weight must be minimized.