What Are Electronic Cooling Devices? Exploring the Different Types and Applications
In the world of electronic devices, heat is a major concern. Excessive heat can cause malfunctions, reduce performance, and even lead to permanent damage. To combat this issue, electronic cooling devices are utilized to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures. In this article, we will explore the different types of electronic cooling devices and their applications in various industries.
1. Understanding the Importance of Electronic Cooling
Before delving into specific cooling devices, it's essential to understand why electronic cooling is crucial. Electronic components generate heat during operation due to resistance, inefficiencies, and power consumption. If this heat is not effectively dissipated, it can lead to performance degradation, premature component failure, and safety hazards. Electronic cooling devices play a vital role in keeping electronics within their optimal temperature range.
2. Heat Sinks: The Workhorses of Electronic Cooling
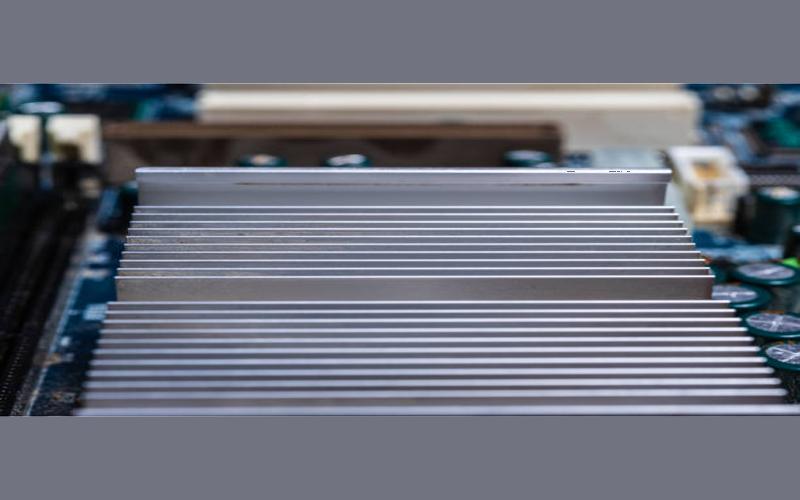
One of the most commonly used electronic cooling devices is the heat sink. A heat sink is a passive cooling solution designed to absorb and dissipate heat from electronic components. It consists of a thermally conductive material, often aluminum or copper, with fins to increase the surface area for heat dissipation. Heat sinks are widely used in computers, power electronics, and LED lighting systems.
3. Fans and Blowers: Enhancing Airflow for Cooling
In many electronic devices, heat sinks alone may not be sufficient to dissipate the heat generated. This is where fans and blowers come into play. These active cooling devices create airflow around the heat sink, helping to carry away the heat more efficiently. Fans are commonly used in desktop computers, servers, and gaming consoles, while blowers are preferred in compact spaces where directed airflow is necessary.
4. Liquid Cooling Systems: Efficient Heat Dissipation
For high-performance electronic devices that generate significant heat, liquid cooling systems offer a more efficient cooling solution. These systems use a liquid, such as water or coolant, to absorb and dissipate heat from the electronic components. Liquid cooling is often seen in gaming PCs, data centers, and high-end servers, where heat dissipation is critical to prevent performance throttling and component damage.
5. Thermoelectric Coolers: Active Cooling Through Temperature Differences
Thermoelectric coolers, also known as Peltier devices, offer active cooling by leveraging the Peltier effect. They consist of two dissimilar semiconductor materials that create a temperature difference when an electric current is applied. This temperature difference enables one side of the device to cool while the other side heats up. Thermoelectric coolers find applications in portable refrigeration, laser diodes, and scientific instruments.
6. Heat Pipes: Efficient Heat Transfer over Long Distances
Heat pipes are heat transfer devices that employ a sealed, hollow tube containing a working fluid, typically a low-boiling-point liquid. When heat is applied, the working fluid vaporizes and travels to the cooler end of the pipe, where it condenses and releases the heat. Heat pipes are efficient in transferring heat over long distances, making them ideal for cooling applications in laptops, smartphones, and aerospace systems.
7. Phase-Change Materials: Harnessing Latent Heat for Cooling
Phase-change materials (PCMs) are substances that can store and release large amounts of latent heat during phase transitions, such as solid to liquid or liquid to gas. PCMs are used in electronic cooling devices to absorb excess heat and undergo a phase change, effectively cooling the surrounding components. These materials are commonly found in electronic enclosures, automotive cooling systems, and thermal management solutions.
8. Cooling Vests: Protecting Electronics and Humans
Electronic cooling devices are not limited to cooling the components themselves but also play a role in protecting humans working in high-heat environments. Cooling vests equipped with embedded cooling elements help regulate body temperature and prevent heat-related illnesses. These vests find applications in industries like firefighting, military operations, and industrial workplaces.
9. Applications in Emerging Technologies
As technology advances, new electronic cooling devices are being developed to cater to emerging applications. For example, in electric vehicles, thermal management systems are crucial to maintain battery efficiency and prolong their lifespan. Advanced cooling solutions, such as direct liquid cooling or immersion cooling, are being explored to tackle the heat challenges in these innovative technologies.
10. The Future of Electronic Cooling Devices
With the constant evolution of electronic devices, the demand for efficient cooling solutions will continue to grow. Researchers and engineers are exploring novel cooling techniques, such as carbon nanotube-based cooling, microfluidic cooling, and even utilizing artificial intelligence to optimize cooling strategies. The future of electronic cooling devices holds exciting possibilities to ensure electronics perform at their best while remaining cool.