The Fundamentals of Heat Dissipation
Aluminium heat sinks are essential components in electronic devices that help dissipate heat to prevent overheating and damage.
Conductive Properties of Aluminium
Aluminium is an ideal material for heat sinks due to its high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to transfer away from the electronic components efficiently.
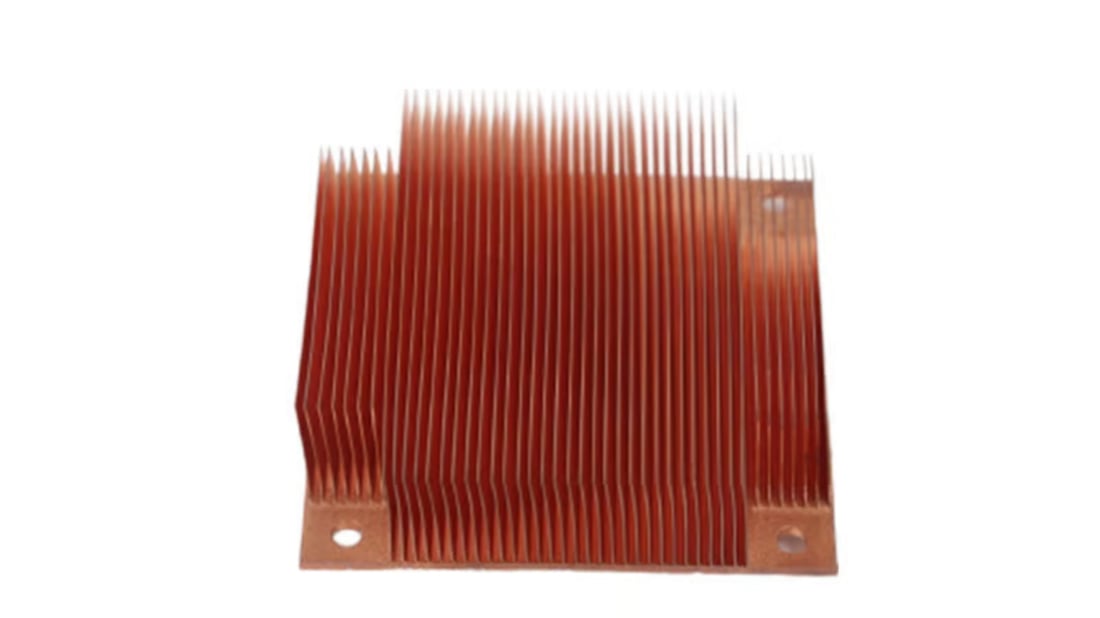
Design and Construction
Heat sinks are designed with fins and a base to maximize surface area for heat dissipation, and are often attached to the heat source using thermal paste or adhesive.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Aluminium heat sinks work through various heat transfer mechanisms such as conduction, convection, and radiation to effectively dissipate heat.
Conduction in Action
Conduction is the primary heat transfer mechanism in aluminium heat sinks, where heat is transferred through direct contact between the heat source and the heat sink.
Utilizing Convection
Convection involves the movement of air or liquid around the heat sink to carry heat away, enhancing the overall cooling efficiency.
Enhancing Heat Radiation
Radiation plays a minor role in heat dissipation for aluminium heat sinks, as they emit thermal radiation to further reduce heat levels.
Efficiency and Performance
Aluminium heat sinks are known for their high efficiency and performance in dissipating heat, making them popular choices in various electronic applications.
Applications in Electronics
Aluminium heat sinks are commonly used in CPUs, GPUs, LED lights, and other electronic devices to regulate temperature and ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Heat Sink
When selecting an aluminium heat sink, factors such as size, shape, and thermal resistance should be considered to match the specific cooling requirements of the device.
Quote Inquiry
Contact us!