The Importance of cold plate cooling
In the world of electronics, heat management is crucial. Excessive heat can cause components to malfunction, leading to decreased performance and even permanent damage. This is where cold plate cooling comes into play. This innovative cooling technique allows for efficient heat dissipation, ensuring that your electronic devices stay cool even under heavy usage. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of cold plate cooling and how it can benefit your electronic systems.
How Does Cold Plate Cooling Work?
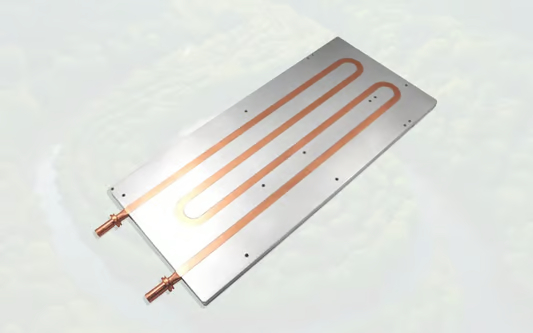
Cold plate cooling, also known as liquid cooling, is a method that uses a plate or heat sink to transfer heat away from a component or system. The plate is typically composed of a thermally conductive material such as copper or aluminum. A cooling fluid, usually water or a refrigerant, flows through channels within the plate, absorbing the heat generated by the electronic components. The heated fluid then circulates to a radiator or heat exchanger where it dissipates the heat into the surrounding environment, allowing the cooled fluid to return to the cold plate and repeat the process.
The Advantages of Cold Plate Cooling
1. Enhanced Heat Dissipation: Cold plate cooling provides superior heat dissipation compared to traditional air cooling methods. The direct contact between the cold plate and the component allows for efficient transfer of heat, resulting in lower operating temperatures.
2. Improved Performance: By keeping electronic components cool, cold plate cooling helps to maintain optimal performance. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency, increased power consumption, and even system failures. Cold plate cooling mitigates these issues, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
3. Compact Design: Cold plate cooling offers a compact solution for thermal management. The flat plate design can be easily integrated into various systems, making it ideal for applications with limited space.
4. Noise Reduction: Unlike traditional cooling methods that rely on fans, cold plate cooling operates silently. This makes it an excellent choice for noise-sensitive environments such as recording studios or medical facilities.
5. Longevity: Excessive heat can significantly shorten the lifespan of electronic components. Cold plate cooling helps to prolong the longevity of devices by maintaining lower operating temperatures and reducing the risk of thermal stress.
Cold Plate Cooling Applications
Cold plate cooling finds applications in a wide range of industries and systems. Some notable examples include:
1. High-Performance Computing: Cold plate cooling is commonly used in data centers and server rooms to keep high-performance computing systems running at optimal temperatures.
2. Electric Vehicles: The efficient heat dissipation offered by cold plate cooling makes it an ideal choice for cooling electric vehicle batteries, power electronics, and charging systems.
3. Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace and defense applications, cold plate cooling is used to cool avionics, radar systems, and other electronic components that operate in demanding conditions.
4. Medical Equipment: Medical devices such as MRI machines, X-ray systems, and laser equipment generate a significant amount of heat. Cold plate cooling helps to ensure reliable and safe operation in these critical healthcare systems.
5. Renewable Energy: Cold plate cooling is utilized in solar inverters, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems to maintain optimal performance and reliability.
The Future of Cold Plate Cooling
Cold plate cooling continues to advance, driven by the ever-increasing demand for efficient thermal management solutions. Ongoing research and development are focused on further improving heat transfer efficiency, reducing system complexity, and optimizing integration into a variety of applications. With the rapid growth of industries such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, and high-performance computing, cold plate cooling is poised to play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic systems.