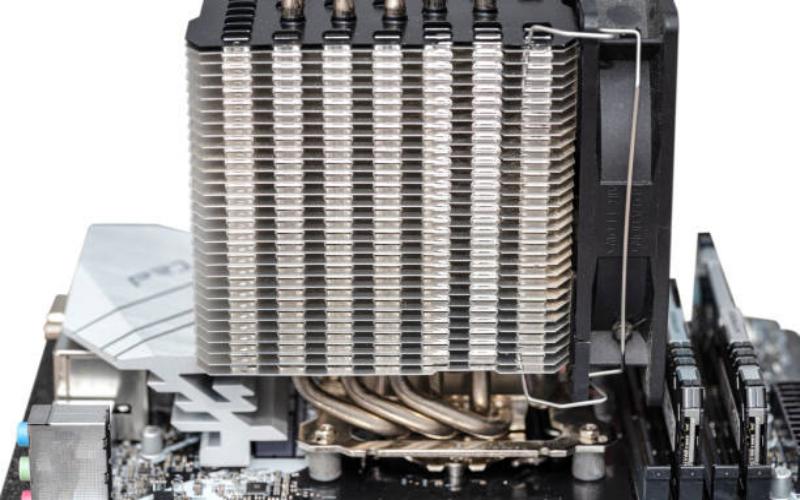
The Basics of Heat Pipe Heat Sink
A heat pipe heat sink is a highly efficient cooling device used in various electronic applications to dissipate heat. It utilizes the principles of heat transfer and phase change to efficiently transfer heat away from the source. This article explores the Principle And Characteristics Of Heat Pipe Heat Sinks, shedding light on their working mechanism, advantages, and applications.
Understanding the Principle of Heat Pipe Heat Sink
The principle behind a heat pipe heat sink is based on the concept of phase change. The heat pipe contains a working fluid, which undergoes a phase change from liquid to vapor and vice versa. When heat is applied to one end of the heat pipe, the working fluid evaporates, absorbing the heat energy. The vapor then travels to the cooler end of the heat pipe, where it condenses, releasing the heat. This continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation allows for efficient heat transfer.
Characteristics of Heat Pipe Heat Sink
Heat pipe heat sinks possess several characteristics that make them a popular choice for thermal management. These characteristics include:
High Thermal Conductivity
Heat pipes have exceptionally high thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 10,000 to 100,000 W/m·K. This high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer across the entire length of the heat pipe, ensuring effective cooling.
Passive Operation
Heat pipe heat sinks operate passively, meaning they do not require any external power source. This makes them reliable, silent, and highly suitable for applications where noise and power consumption are concerns.
Compact and Lightweight
Heat pipe heat sinks are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Their small size allows for easy integration into electronic devices without adding significant weight or bulk.
High Heat Flux Handling Capacity
Heat pipe heat sinks can handle high heat fluxes, making them suitable for cooling high-power electronic components. They can efficiently dissipate heat from hotspots and distribute it across a larger surface area, preventing thermal damage.
Flexible Form Factors
Heat pipe heat sinks can be designed in various shapes and sizes to fit specific application requirements. They can be straight, bent, or even embedded within other heat sink structures, providing flexibility in thermal design.
Low Thermal Resistance
Heat pipe heat sinks have low thermal resistance, allowing for efficient heat transfer even over long distances. This characteristic ensures that heat is rapidly removed from the heat source, preventing temperature buildup and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Reliability and Longevity
Heat pipe heat sinks are highly reliable and have a long operational lifespan. They have no moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and are not prone to wear and tear. This makes them a durable solution for thermal management.
Applications of Heat Pipe Heat Sink
Heat pipe heat sinks find applications in various industries and electronic devices, including:
Computer Systems
Heat pipe heat sinks are commonly used in computer systems to cool central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), and other high-performance components. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring system stability and longevity.
LED Lighting
LED lighting generates significant heat, which can negatively impact their performance and lifespan. Heat pipe heat sinks effectively dissipate heat from LED bulbs, enhancing their efficiency and extending their lifespan.
Solar Panels
Solar panels operate more efficiently at lower temperatures. Heat pipe heat sinks help remove excess heat from solar panels, preventing performance degradation and ensuring maximum energy conversion.
Telecommunications
Heat pipe heat sinks play a crucial role in cooling telecommunications equipment, such as routers, switches, and power amplifiers. Their compact size and high thermal conductivity make them an ideal choice for these applications.
Automotive Electronics
Automotive electronics, including engine control units (ECUs) and power electronics, generate significant heat. Heat pipe heat sinks efficiently dissipate this heat, ensuring reliable operation and preventing premature failure.
Conclusion
Heat pipe heat sinks are a versatile and efficient cooling solution, offering high thermal conductivity, passive operation, compact form factors, and reliability. Their application spans across various industries and electronic devices, providing effective heat management and ensuring optimal performance. Understanding the principles and characteristics of heat pipe heat sinks is crucial for engineers and designers seeking efficient thermal solutions in their projects.